Reduced Levels of miR-145-3p Drive Cell Cycle Progression in Advanced High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 39594652
- PMCID: PMC11592657
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13221904
Reduced Levels of miR-145-3p Drive Cell Cycle Progression in Advanced High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
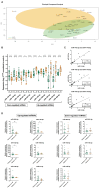
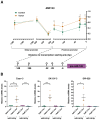
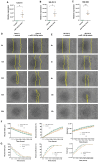
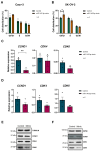
High-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) is the most lethal form of gynecologic cancer, with limited treatment options and a poor prognosis. Epigenetic factors, such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and DNA methylation, play pivotal roles in cancer progression, yet their specific contributions to HGSOC remain insufficiently understood. In this study, we performed comprehensive high-throughput analyses to identify dysregulated miRNAs in HGSOC and investigate their epigenetic regulation. Analysis of tissue samples from advanced-stage HGSOC patients revealed 20 differentially expressed miRNAs, 11 of which were corroborated via RT-qPCR in patient samples and cancer cell lines. Among these, miR-145-3p was consistently downregulated post-neoadjuvant therapy and was able to distinguish tumoural from control tissues. Further investigation confirmed that DNA methylation controls MIR145 expression. Functional assays showed that overexpression of miR-145-3p significantly reduced cell migration and induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest by modulating the cyclin D1-CDK4/6 pathway. These findings suggest that miR-145-3p downregulation enhances cell proliferation and motility in HGSOC, implicating its restoration as a potential therapeutic target focused on G1/S phase regulation in the treatment of HGSOC.
Keywords: DNA methylation; cell cycle proliferation; cyclin D1-CDK4/6 pathway; high-grade serous ovarian cancer; miR-145-3p; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 7 July 2022)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr.
-
- Marí-Alexandre J., Carcelén A.P., Agababyan C., Moreno-Manuel A., García-Oms J., Calabuig-Fariñas S., Gilabert-Estellés J. Interplay Between MicroRNAs and Oxidative Stress in Ovarian Conditions with a Focus on Ovarian Cancer and Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:5322. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ledermann J.A., Raja F.A., Fotopoulou C., Gonzalez-Martin A., Colombo N., Sessa C. Newly diagnosed and relapsed epithelial ovarian carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013;24((Suppl. S6)):vi24–vi32. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt333. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- PI17/01945/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI22/01872/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- GV/2020/200/Generalitat Valenciana
- Prize SOGCV 2019/"Sociedad de Obstetricia y Ginecología de la Comunidad Valenciana" (SOGCV)
- Prize FIHGUV 2019/Fundacio Investigacio Hospital General Universitari De Valencia
- ACIF/2020/216/Generalitat Valenciana
- Pre-doctoral grant 2023 Valencia/Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer
- Pre-doctoral grant 2022 Valencia/Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer
- CNS2022-135933/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- PID2020-114459RA-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- PLEC2022-009246/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- Grant/Fundación Ramón Areces
- Grant/Amunt Contra el Càncer
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

