Modulation of the Immune Environment in Glioblastoma by the Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 39594997
- PMCID: PMC11591702
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12112429
Modulation of the Immune Environment in Glioblastoma by the Gut Microbiota
Abstract
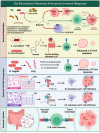
Studies increasingly support the role of the gut microbiota in glioma development and treatment, although the exact mechanisms remain unclear. Research indicates that the gut microbiota can influence glioma progression, response to therapies, and the effectiveness of treatments like immunotherapy, with certain microbial compositions being linked to better outcomes. Additionally, the gut microbiota impacts the tumor microenvironment, affecting both tumor growth and the response to treatment. This review will explore glioma, the gut microbiota, and how their interaction shapes glioma development and therapy responses. Additionally, this review examines the influence of gut microbiota metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and tryptophan, on glioma development and treatment. It also explores gut microbiome signaling via pattern recognition receptors, and the role of molecular mimicry between microbial and tumor antigens in glioblastoma, and if these interactions affect glioma development and treatment.
Keywords: glioblastoma; glioma; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no knowledge of any conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wiertsema S.P., van Bergenhenegouwen J., Garssen J., Knippels L.M.J. The Interplay between the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System in the Context of Infectious Diseases throughout Life and the Role of Nutrition in Optimizing Treatment Strategies. Nutrients. 2021;13:886. doi: 10.3390/nu13030886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

