Angiopoietin II in Critically Ill Septic Patients: A Post Hoc Analysis of the DRAK Study
- PMID: 39595003
- PMCID: PMC11591998
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12112436
Angiopoietin II in Critically Ill Septic Patients: A Post Hoc Analysis of the DRAK Study
Abstract
Introduction: Angiopoietin II (Ang-II) plays a pivotal role in the development of microcirculatory dysfunction as it provokes endothelial barrier disruption in patients with sepsis or septic shock. In particular, those with acute kidney injury show high Ang-II concentrations. So far, it is unclear which covariates influence Ang-II concentration in the early phase of sepsis, especially if extracorporeal therapies also do.
Methods: Ang-II concentrations were measured in 171 patients with sepsis after the first day of antibiotic treatment between 03/2013 and 01/2015. Ang-II was correlated with potential influencing factors (Spearman correlation). A multivariate model was established including the significant correlating parameters. The Mann-Whitney U test and the Kruskal-Wallis test were used to detect significant differences in Ang-II concentration.
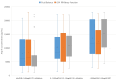
Results: The median Ang-II concentration was 8015 pg/mL (interquartile range (IQR): 5024-14,185). A total of forty patients were treated with kidney replacement therapy (KRT) and 20 were supported by venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (vv-ECMO). Sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score (r = 0.541), creatinine clearance (r = -0.467), urinary output (r = -0.289), interleukin (IL)-6 (r = 0.529), C-reactive protein (CRP) (r = 0.241), platelet count (r = -0.419), bilirubin (r = 0.565), lactate (r = 0.322), KRT (r = 0.451), and fluid balance (r = 0.373) significantly correlated with Ang-II concentration and were included in the multivariate model. There, creatinine clearance (p < 0.01, b = -26.3, 95% confidence interval (CI) -41.8--10.8), fluid balance (p = 0.002, b = 0.92, 95% CI 0.33-1.51), and CRP (p = 0.004, b = 127.6, 95% CI 41.6-213.7) were associated with Ang-II concentration. Furthermore, patients with KRT (median: 15,219 pg/mL, IQR: 10,548-20,270) had significantly (p < 0.01) higher Ang-II concentrations than those with vv-ECMO support (median: 6412 pg/mL, IQR: 5246-10,257) or those without extracorporeal therapy (median: 7156 pg/mL, IQR: 4409-12,741).
Conclusion: Increased CRP, positive fluid balance, and impaired kidney function were associated with higher Ang-II concentrations in critically ill patients in the early stage of sepsis in this post hoc analysis. In particular, patients with KRT had very high Ang-II concentrations, whereas the use of vv-ECMO was not related to higher Ang-II concentrations. The significance for clinical practice should be clarified by a prospective study with standardized measurements.
Keywords: angiopoietin-2; creatinine clearance; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO); fluid balance; kidney replacement therapy (KRT); sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
U.L. received consulting honoraria from Cytosorbents Europe GmbH and is part of an advisory board of Roche Diagnostics International Ltd. C.S. received speakers’ honoraria from Cytosorbents Europe GmbH. Author Johannes Zander was employed by the company Labor Dr. Brunner. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anticoagulation and Transfusions Management in Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Assessment of Factors Associated With Transfusion Requirements and Mortality.J Intensive Care Med. 2019 Aug;34(8):630-639. doi: 10.1177/0885066617706339. Epub 2017 May 1. J Intensive Care Med. 2019. PMID: 28460592
-
[The levels of angiopoietin-2 in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome and its value on prognosis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Nov;26(11):804-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.11.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 25399895 Chinese.
-
Outcomes of critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients requiring kidney replacement therapy: A retrospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 20;9:1027586. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1027586. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36341239 Free PMC article.
-
Early acute kidney injury and transition to renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 requiring veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.Ann Intensive Care. 2023 Nov 24;13(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13613-023-01205-x. Ann Intensive Care. 2023. PMID: 37999776 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the treatment of poisoned patients.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2013 Jun;51(5):385-93. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2013.800876. Epub 2013 May 23. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23697460 Review.
Cited by
-
Diffusion tensor imaging reveals myocardial architectural differences between porcine and primate hearts with potential implications for cardiac xenotransplantation.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28696. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14368-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770390 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

