Correction: Chen et al. Heteronemin Suppresses Lymphangiogenesis Through ARF-1 and MMP-9/VE-Cadherin/Vimentin. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1109
- PMID: 39595215
- PMCID: PMC11591881
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12112609
Correction: Chen et al. Heteronemin Suppresses Lymphangiogenesis Through ARF-1 and MMP-9/VE-Cadherin/Vimentin. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1109
Abstract
Error in Affiliation [...].
Figures

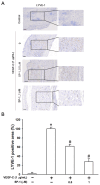

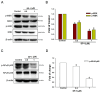
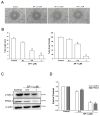
Erratum for
-
Heteronemin Suppresses Lymphangiogenesis through ARF-1 and MMP-9/VE-Cadherin/Vimentin.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 29;9(9):1109. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091109. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572295 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

