Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis Links DNMT3B and PFKFB4 Transcriptional Profiles with Metastatic Traits in Hepatoblastoma
- PMID: 39595571
- PMCID: PMC11591731
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14111394
Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis Links DNMT3B and PFKFB4 Transcriptional Profiles with Metastatic Traits in Hepatoblastoma
Erratum in
-
Correction: Desterke et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis Links DNMT3B and PFKFB4 Transcriptional Profiles with Metastatic Traits in Hepatoblastoma. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1394.Biomolecules. 2025 May 27;15(6):769. doi: 10.3390/biom15060769. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563546 Free PMC article.
Abstract
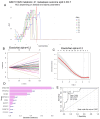
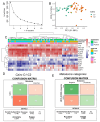
Hepatoblastoma is the most common primary liver cancer in children. Poor outcomes are primarily associated with patients who have distant metastases. Using the Mammalian Metabolic Enzyme Database, we investigated the overexpression of metabolic enzymes in hepatoblastoma tumors compared to noncancerous liver tissue in the GSE131329 transcriptome dataset. For the overexpressed enzymes, we applied ElasticNet machine learning to assess their predictive value for metastasis. A metabolic expression score was then computed from the significant enzymes and integrated into a clinical-biological logistic regression model. Forty-one overexpressed enzymes distinguished hepatoblastoma tumors from noncancerous liver tissues. Eighteen of these enzymes predicted metastasis status with an AUC of 0.90, demonstrating 85.7% sensitivity and 92.3% specificity. ElasticNet machine learning identified DNMT3B and PFKFB4 as key predictors of metastasis. Univariate analyses confirmed the significance of these enzymes, with respective p-values of 0.0058 and 0.0091. A metabolic score based on DNMT3B and PFKFB4 expression discriminated metastasis status and high-risk CHIC scores (p-value = 0.005). The metabolic score was more sensitive than the C1/C2 classifier in predicting metastasis (accuracy: 0.72 vs. 0.55). In a regression model integrating the metabolic score with epidemiological parameters (gender, age at diagnosis, histological type, and clinical PRETEXT stage), the metabolic score was confirmed as an independent adverse predictor of metastasis (p-value = 0.003, odds ratio: 2.12). This study identified the dual overexpression of PFKFB4 and DNMT3B in hepatoblastoma patients at risk of metastasis (high-risk CHIC classification). The combined tumor expression of DNMT3B and PFKFB4 was used to compute a metabolic score, which was validated as an independent predictor of metastatic status in hepatoblastoma.
Keywords: CHIC risk; DNA methylation; epigenetics; glycolysis; hepatoblastoma; metabolism; metastasis; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sasaki F., Matsunaga T., Iwafuchi M., Hayashi Y., Ohkawa H., Ohira M., Okamatsu T., Sugito T., Tsuchida Y., Toyosaka A., et al. Outcome of Hepatoblastoma Treated with the JPLT-1 (Japanese Study Group for Pediatric Liver Tumor) Protocol-1: A Report from the Japanese Study Group for Pediatric Liver Tumor. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2002;37:851–856. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2002.32886. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meyers R.L., Maibach R., Hiyama E., Häberle B., Krailo M., Rangaswami A., Aronson D.C., Malogolowkin M.H., Perilongo G., von Schweinitz D., et al. Risk-Stratified Staging in Paediatric Hepatoblastoma: A Unified Analysis from the Children’s Hepatic Tumors International Collaboration. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:122–131. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30598-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

