Structure-Tissue Exposure/Selectivity Relationship (STR) on Carbamates of Cannabidiol
- PMID: 39595958
- PMCID: PMC11593952
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252211888
Structure-Tissue Exposure/Selectivity Relationship (STR) on Carbamates of Cannabidiol
Abstract
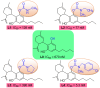
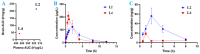
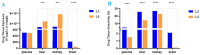
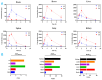
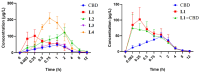
The structure-tissue exposure/selectivity relationship (STR) aids in lead optimization to improve drug candidate selection and balance clinical dose, efficacy, and toxicity. In this work, butyrocholinesterase (BuChE)-targeted cannabidiol (CBD) carbamates were used to study the STR in correlation with observed efficacy/toxicity. CBD carbamates with similar structures and same molecular target showed similar/different pharmacokinetics. L2 and L4 had almost same plasma exposure, which was not correlated with their exposure in the brain, while tissue exposure/selectivity was correlated with efficacy/safety. Structural modifications of CBD carbamates not only changed drug plasma exposure, but also altered drug tissue exposure/selectivity. The secondary amine of carbamate can be metabolized into CBD, while the tertiary amine is more stable. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) parameters can be used to predict STR. Therefore, STR can alter drug tissue exposure/selectivity in normal tissues, impacting efficacy/toxicity. The drug optimization process should balance the structure-activity relationship (SAR) and STR of drug candidates for improving clinical trials.
Keywords: butyrocholinesterase; cannabidiol; carbamate; drug development and optimization; structure–activity relationship (SAR); structure–tissue exposure/selectivity relationship (STR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure‒tissue exposure/selectivity relationship (STR) correlates with clinical efficacy/safety.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 May;12(5):2462-2478. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.02.015. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35646532 Free PMC article.
-
Novel cannabidiol-carbamate hybrids as selective BuChE inhibitors: Docking-based fragment reassembly for the development of potential therapeutic agents against Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Nov 5;223:113735. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113735. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34371367
-
Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it?Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jul;12(7):3049-3062. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35865092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabidiol-2',6'-dimethyl ether, a cannabidiol derivative, is a highly potent and selective 15-lipoxygenase inhibitor.Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Aug;37(8):1733-7. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.026930. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009. PMID: 19406952
-
Clinical implications of trials investigating drug-drug interactions between cannabidiol and enzyme inducers or inhibitors or common antiseizure drugs.Epilepsia. 2020 Sep;61(9):1854-1868. doi: 10.1111/epi.16674. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Epilepsia. 2020. PMID: 32918835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verma S., Pathak R.K. Bioinformatics Methods and Applications. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2022. Chapter 16—Discovery and optimization of lead molecules in drug designing; pp. 253–267.
-
- Davies M., Jones R.D.O., Grime K., Jansson-Löfmark R., Fretland A.J., Winiwarter S., Morgan P., McGinnity D.F. Improving the Accuracy of Predicted Human Pharmacokinetics: Lessons Learned from the AstraZeneca Drug Pipeline Over Two Decades. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020;41:390–408. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2020.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

