Bioactive Hybrids Containing Artificial Cell Membranes and Phyto-Gold-Silver Chloride Bio-Nanoparticles
- PMID: 39596000
- PMCID: PMC11593899
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252211929
Bioactive Hybrids Containing Artificial Cell Membranes and Phyto-Gold-Silver Chloride Bio-Nanoparticles
Abstract
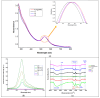
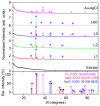
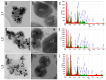
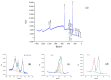
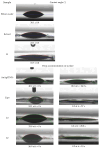
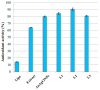
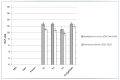
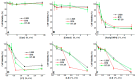
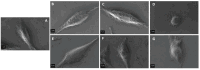
This research targets the need for eco-friendly strategies in the synthesis of bioactive materials, addressing the importance of valorization of vegetal waste. This study focuses on developing biohybrids containing biomimetic lipid vesicles and phytosynthesized gold-silver chloride nanoparticles (AuAgCl NPs) derived from Achillea millefolium L. extract. By leveraging the natural antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the plant, the research proposes a sustainable approach to creating materials with potential biomedical applications. The biomimetic membranes were loaded with chlorophyll a, a natural spectral marker. Three types of bioactive materials (biohybrids) were developed by varying the lipid vesicle/AuAgCl NP ratio. Optical (UV-Vis, fluorescence emission, FTIR), structural (XRD), elemental (EDX, XPS), and morphological (TEM) studies were performed to characterize the bio-developed materials. The hydrophobic/hydrophilic characteristics of the samples were investigated by measuring the water contact angle, and their size was estimated by DLS and TEM. Zeta potential measurements were used to evaluate the physical stability of phyto-developed particles. Antioxidant properties of phyto-particles were investigated through the chemiluminescence technique. The obtained biomaterials exhibited high antioxidant activity and antiproliferative activity against HT-29 and B-16 cancer cells. Therapeutic index values were calculated for each biohybrid. Additionally, the bio-prepared hybrids revealed biocidal action against Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. The phyto-developed biomaterials are promising in biomedical applications, particularly as adjuvants in cancer therapy.
Keywords: Achillea millefolium L.; antioxidant activity; antimicrobial properties; antiproliferative activity; gold–silver chloride nanoparticles; phytosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Villalva M., Silvan J.M., Alarcón-Cavero T., Villanueva-Bermejo D., Jaime L., Santoyo S., Martinez-Rodriguez A.J. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antibacterial Properties of an Achillea millefolium L. Extract and Its Fractions Obtained by Supercritical Anti-Solvent Fractionation against Helicobacter pylori. Antioxidants. 2022;11:1849. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101849. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ancuceanu R., Hovanet M.V., Anghel A.-I., Dinu M.A. Millefolium L. in pharmacy. What should a pharmacist know? Rom. J. Pharm. Pract. 2023;16:57–71. doi: 10.37897/RJPhP.2023.3-4.4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

