Direct Effects of the Janus Kinase Inhibitor Baricitinib on Sensory Neurons
- PMID: 39596013
- PMCID: PMC11593535
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252211943
Direct Effects of the Janus Kinase Inhibitor Baricitinib on Sensory Neurons
Abstract
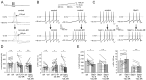
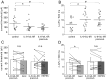
Therapeutically, the Janus kinase (Jak) 1/Jak2 inhibitor baricitinib reduces the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis and may also reduce pain. Here, we investigated whether baricitinib directly affects joint nociceptors. We recorded action potentials from nociceptive C- and A∂-fibers of the normal and inflamed knee joint in anesthetized rats to monitor their responses to innocuous and noxious joint rotation. In isolated and cultured dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, we examined Stat3 activation using Western blots and monitored excitability using patch-clamp recordings. Intra-articular injection of baricitinib did not alter C- and A∂-fiber responses to innocuous and noxious rotations of the normal knee but reduced C-fiber responses to these stimuli in inflamed joints. Baricitinib prevented the increase in C-fiber responses to joint rotation evoked by interleukin (IL)-6 plus soluble interleukin-6 receptor (sIL-6R) but not the increase evoked by TNF. In DRG neurons, baricitinib blocked Stat3 activation by hyper-IL-6, and baricitinib or the Stat3 inhibitor Sta21 prevented induction of hyperexcitability by IL-6 plus sIL-6R. Thus, neuronal Jaks are involved in the generation of C-fiber hyperexcitability induced by inflammation and IL-6. Pain reduction by baricitinib may result, at least in part, from direct effects on joint nociceptors.
Keywords: DRG neurons; Jak inhibitor; Stat3; TNF; baricitinib; interleukin-6; joint pain; neuronal Jak; nociceptor; pain sensitization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
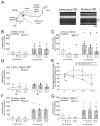
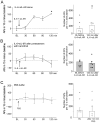
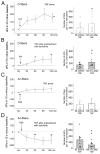
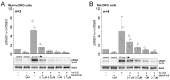
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

