Infertility, IL-17, IL-33 and Microbiome Cross-Talk: The Extended ARIA-MeDALL Hypothesis
- PMID: 39596052
- PMCID: PMC11594021
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252211981
Infertility, IL-17, IL-33 and Microbiome Cross-Talk: The Extended ARIA-MeDALL Hypothesis
Abstract
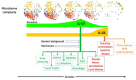
Infertility, defined as the inability to obtain pregnancy after 12 months of regular unprotected sexual intercourse, has increased in prevalence over the past decades, similarly to chronic, allergic, autoimmune, or neurodegenerative diseases. A recent ARIA-MeDALL hypothesis has proposed that all these diseases are linked to dysbiosis and to some cytokines such as interleukin 17 (IL-17) and interleukin 33 (IL-33). Our paper suggests that endometriosis, a leading cause of infertility, is linked to endometrial dysbiosis and two key cytokines, IL-17 and IL-33, which interact with intestinal dysbiosis. Intestinal dysbiosis contributes to elevated estrogen levels, a primary factor in endometriosis. Estrogens strongly activate IL-17 and IL-33, supporting the existence of a gut-endometrial axis as a significant contributor to infertility.
Keywords: IL-17; IL-33; dysbiosis; endometriosis; estrogens; infertility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Geyter C., Calhaz-Jorge C., Kupka M.S., Wyns C., Mocanu E., Motrenko T., Scaravelli G., Smeenk J., Vidakovic S., Goossens V., et al. ART in Europe, 2014: Results generated from European registries by ESHRE: The European IVF-monitoring Consortium (EIM) for the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) Hum. Reprod. 2018;33:1586–1601. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey242. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fabozzi G., Verdone G., Allori M., Cimadomo D., Tatone C., Stuppia L., Franzago M., Ubaldi N., Vaiarelli A., Ubaldi F.M., et al. Personalized Nutrition in the Management of Female Infertility: New Insights on Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation. Nutrients. 2022;14:1918. doi: 10.3390/nu14091918. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous