Caffeine: A Multifunctional Efficacious Molecule with Diverse Health Implications and Emerging Delivery Systems
- PMID: 39596082
- PMCID: PMC11593559
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212003
Caffeine: A Multifunctional Efficacious Molecule with Diverse Health Implications and Emerging Delivery Systems
Abstract
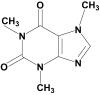
Natural caffeine is found in many plants, including coffee beans, cacao beans, and tea leaves. Around the world, many beverages, including coffee, tea, energy drinks, and some soft drinks, have this natural caffeine compound. This paper reviewed the results of meta-studies on caffeine's effects on chronic diseases. Of importance, many meta-studies have shown that regularly drinking caffeine or caffeinated coffee significantly reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, and Parkinson's disease. Based on the health supplements of caffeine, this review summarizes various aspects related to the application of caffeine, including its pharmacokinetics, and various functional health benefits of caffeine, such as its effects on the central nervous system. The importance of caffeine and its use in alleviating or treating cancer, diabetes, eye diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cardiovascular diseases is also discussed. Overall, consuming caffeine daily in drinks containing antioxidant and neuroprotective properties, such as coffee, prevents progressive neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Furthermore, to effectively deliver caffeine to the body, recently developed nanoformulations using caffeine, for instance, nanoparticles, liposomes, etc., are summarized along with regulatory and safety considerations for caffeine. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommended that healthy adults consume up to 400 mg of caffeine per day or 5~6 mg/kg body weight. Since a cup of coffee contains, on average, 100 to 150 mg of coffee, 1 to 3 cups of coffee may help prevent chronic diseases. Furthermore, this review summarizes various interesting and important areas of research on caffeine and its applications related to human health.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; autoimmune diseases; caffeine; metabolic disorders; migraine; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Kyung Eun Lee was employed by the company Sunforce Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Banwo K., Olojede A., Adesulu-Dahunsi A., Verma D., Thakur M., Tripathy S., Singh S., Patel A., Gupta A., Aguilar C., et al. Functional importance of bioactive compounds of foods with Potential Health Benefits: A review on recent trends. Food Biosci. 2021;43:101320. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101320. - DOI
-
- Vinayagam R., Lee K., Ambati D.R.R., Gundamaraju R., Hassanien M., Kang S.G. Recent development in black garlic: Nutraceutical applications and health-promoting phytoconstituents. Food Rev. Int. 2021;39:1–21. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2021.2012797. - DOI
-
- Gomez-Bruton A., Marin-Puyalto J., Muñiz-Pardos B., Matute-Llorente A., Del Coso J., Gomez-Cabello A., Vicente-Rodriguez G., Casajus J.A., Lozano-Berges G. Does Acute Caffeine Supplementation Improve Physical Performance in Female Team-Sport Athletes? Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021;13:3663. doi: 10.3390/nu13103663. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical