Unveiling Biomarkers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Bioinformatics: The Role of SPP1 and KRT78
- PMID: 39596132
- PMCID: PMC11594244
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212062
Unveiling Biomarkers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Bioinformatics: The Role of SPP1 and KRT78
Abstract
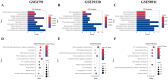
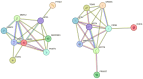
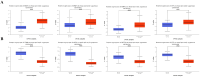
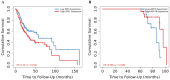
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the most common form of head and neck cancer, ranking sixth in global cancer incidence. Identifying molecular drivers of tumorigenesis and metastasis is essential for early detection and treatment. This study analyzed gene expression profiles from three datasets (GSE6791, GSE29330, and GSE58911) to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in HNSCC. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analyses were employed to functionally annotate these DEGs. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed for selecting hub genes using the STRING database. Finally, hub gene and protein expression levels were evaluated in patients with HNSCC, along with their association with overall survival. Our analysis identified twenty-eight co-DEGs comprising eight up-regulated and twenty down-regulated genes, primarily involved in extracellular matrix (ECM) organization, proteolysis, ECM disassembly, and keratinization processes. Furthermore, the PPI network revealed eight hub genes based on their high degree of connectivity. Notably, SPP1 demonstrated up-regulation, while KRT78 was down-regulated in HNSCC. Remarkably, the expression levels of these hub genes correlated with tumor grade, clinical cancer stage, and poor prognosis in HNSCC. Our findings hold significant clinical potential for early diagnosis and the development of novel therapeutic targets for patients with HNSCC.
Keywords: KRT78; SPP1; bioinformatics; biomarker; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bhat G.R., Hyole R.G., Li J. Advances in Cancer Research. Vol. 152. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021. Head and Neck Cancer: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives; pp. 67–102. - PubMed
-
- MICHA R. Checkpoint Immunotherapy in Head and Neck Cancers. Physiol. Behav. 2017;176:100–106. doi: 10.1177/0022146515594631. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NRF-2020R1A2C1006398; RS-2024-00441029/Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea Ministry of Science and Technology
- 2017R1A2B2003575; 2020R1C1C1012288/ICT and Future Planning
- IITP-2024-2020-0-01819/ICT Creative Consilience program
- HI17C0387; HR22C1302/Korea Health Technology R&D Project
- RS-2023-00246305/Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea Ministry of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

