Functional Food Nutrients, Redox Resilience Signaling and Neurosteroids for Brain Health
- PMID: 39596221
- PMCID: PMC11594618
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212155
Functional Food Nutrients, Redox Resilience Signaling and Neurosteroids for Brain Health
Abstract
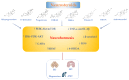
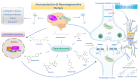
The interplay between functional food nutrients and neurosteroids has garnered significant attention for its potential to enhance stress resilience in health and/or disease. Several bioactive nutrients, including medicinal herbs, flavonoids, and bioavailable polyphenol-combined nanoparticles, as well as probiotics, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, have been shown to improve blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction, endogenous neurosteroid homeostasis and brain function. These nutrients can inhibit oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, which are linked to the pathogenesis of various neurological disorders. Interestingly, flavonoids exhibit dose-dependent effects, activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway at the physiological/low dose (neurohormesis). This leads to the upregulation of antioxidant phase II genes and proteins such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and sirtuin-1 (Sirt1), which are activated by curcumin and resveratrol, respectively. These adaptive neuronal response mechanisms help protect against reactive oxygen species (ROS) and neurotoxicity. Impaired Nrf2 and neurosteroid hormone signaling in the brain can exacerbate selective vulnerability to neuroinflammatory conditions, contributing to the onset and progression of neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, anxiety and depression and other neurological disorders, due to the vulnerability of neurons to stress. This review focuses on functional food nutrients targeting Nrf2 antioxidant pathway and redox resilience genes to regulate the neurosteroid homeostasis and BBB damage associated with altered GABAergic neurotransmission. By exploring the underlying molecular mechanisms using innovative technologies, we aim to develop promising neuroprotective strategies and personalized nutritional and neuroregenerative therapies to prevent or attenuate oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, ultimately promoting brain health.
Keywords: GABA signaling; Nrf2 pathway; central nervous system disorders; cerebral organoids; functional food nutrients; neurohormesis; neuroinflammation; neurosteroids; oxidative stress; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Marx C.E., Stevens R.D., Shampine L.J., Uzunova V., Trost W.T., Butterfield M.I., Massing M.W., Hamer R.M., Morrow A.L., Lieberman J.A. Neuroactive steroids are altered in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: Relevance to pathophysiology and therapeutics. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:1249–1263. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300952. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

