COVID-19 in Children and Vitamin D
- PMID: 39596272
- PMCID: PMC11594876
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212205
COVID-19 in Children and Vitamin D
Abstract
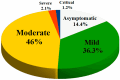
In December 2019, the so-called "coronavirus disease 2019" (COVID-19) began. This disease is characterized by heterogeneous clinical manifestations, ranging from an asymptomatic process to life-threatening conditions associated with a "cytokine storm". This article (narrative review) summarizes the epidemiologic characteristics and clinical manifestations of COVID-19 and multi-system inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). The effect of the pandemic confinement on vitamin D status and the hypotheses proposed to explain the age-related difference in the severity of COVID-19 are discussed. The role of vitamin D as a critical regulator of both innate and adaptive immune responses and the COVID-19 cytokine storm is analyzed. Vitamin D and its links to both COVID-19 (low levels of vitamin D appear to worsen COVID-19 outcomes) and the cytokine storm (anti-inflammatory activity) are detailed. Finally, the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 is evaluated, but the evidence supporting vitamin D supplementation as an adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 remains uncertain.
Keywords: COVID-19; MIS-C; SARS-CoV-2 infection; vitamin D; vitamin D deficiency; vitamin D insufficiency; vitamin D supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao S., Zhuang Z., Ran J., Lin J., Yang G., Yang L., He D. The association between domestic train transportation and novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak in China from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven correlational report. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020;33:101568. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101568. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous