Molecules That Have Rarely Been Studied in Lymphatic Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 39596293
- PMCID: PMC11594919
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212226
Molecules That Have Rarely Been Studied in Lymphatic Endothelial Cells
Abstract
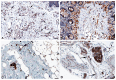
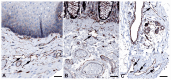
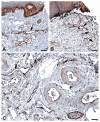
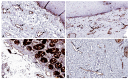
A number of standard molecules are used for the molecular and histological characterization of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), including lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1), Podoplanin (D2-40), VEGFR3, Prospero homeobox protein 1 (PROX1), and CD31. The number of molecules whose mutations cause lymphatic malformations or primary congenital lymphedema is considerable, but the majority of these diseases have not yet been characterized at the molecular level. Therefore, there is still considerable scope for molecular and functional studies of the lymphatic vasculature. Using RNASeq, we have previously characterized lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. We used this information to compare it with immunohistochemical data. We carried out some of the immunohistology ourselves, and systematically studied the Human Protein Atlas, a cell and tissue database based in Sweden. Here we describe molecules that are expressed at RNA and protein levels in LECs, hoping to stimulate future functional studies of these molecules.
Keywords: ANKRD37; CAV1; CAV2; CD59; CNN3; DYSF; KANK3; MARCKSL1; MMRN1; NXN; SPTAN1; SPTBN1; lymphatic endothelial cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this study received funding from Verein zur Förderung der Lymphologie e.V., 79856 Hinterzarten, Germany. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures
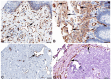
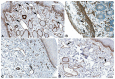
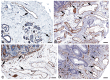
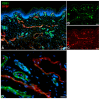
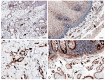
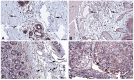
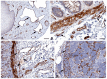
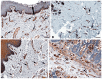
References
-
- Rusznyák I., Földi M., Szabó G. Lymphologie. Physiologie und Pathologie der Lymphgefäße und des Lymphkreislaufes. Akadémiai Kiadó; Budapest, Hungary: 1969.
-
- Asellius G. De Lactibus, Sive Lacteis Venis, Quarto Vasorum Mesaraicorum Genere, Novo Invento Gasparis Asellii Cremonensis. Ex Officina Iohannis Maire 1640; Milan, Italy: 1627.
-
- Mascagni P. Vasorum Lymphaticorum Corporis Humani, Historia et Ichnographia; Senis: Ex Typographia Pazzini Carli. 1787. [(accessed on 5 November 2024)]. Available online: https://archive.org/details/ldpd_11735328_000/page/n7/mode/2up.
-
- Rudbeck O. Nova Exercitatio Anatomica, Exhibens Ductos Hepaticos Aquosos, et Vasa Glandularum Serosa (1653) Almquist and Wiksells; Uppsala, Sweden: 1930.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

