Drug Discovery in the Age of Artificial Intelligence: Transformative Target-Based Approaches
- PMID: 39596300
- PMCID: PMC11594879
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212233
Drug Discovery in the Age of Artificial Intelligence: Transformative Target-Based Approaches
Abstract
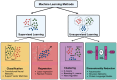
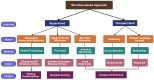
The complexities inherent in drug development are multi-faceted and often hamper accuracy, speed and efficiency, thereby limiting success. This review explores how recent developments in machine learning (ML) are significantly impacting target-based drug discovery, particularly in small-molecule approaches. The Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES), which translates a chemical compound's three-dimensional structure into a string of symbols, is now widely used in drug design, mining, and repurposing. Utilizing ML and natural language processing techniques, SMILES has revolutionized lead identification, high-throughput screening and virtual screening. ML models enhance the accuracy of predicting binding affinity and selectivity, reducing the need for extensive experimental screening. Additionally, deep learning, with its strengths in analyzing spatial and sequential data through convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), shows promise for virtual screening, target identification, and de novo drug design. Fragment-based approaches also benefit from ML algorithms and techniques like generative adversarial networks (GANs), which predict fragment properties and binding affinities, aiding in hit selection and design optimization. Structure-based drug design, which relies on high-resolution protein structures, leverages ML models for accurate predictions of binding interactions. While challenges such as interpretability and data quality remain, ML's transformative impact accelerates target-based drug discovery, increasing efficiency and innovation. Its potential to deliver new and improved treatments for various diseases is significant.
Keywords: drug discovery; general adversarial networks; graph neural networks; phenotypic approaches; random forests; target-based approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Foote K.D. A brief history of machine learning. Dataversity. Mar 3, 2019.
-
- Qiu X., Parcollet T., Fernandez-Marques J., Gusmao P.P., Gao Y., Beutel D.J., Topal T., Mathur A., Lane N.D. A first look into the carbon footprint of federated learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023;24:1–23.
-
- Nailwal K., Durgapal S., Dasauni K., Nailwal T.K. AI: Catalyst for Drug Discovery and Development. In: Bose S., Shukla A.C., Baig M.R., Banerjee S., editors. Concepts in Pharmaceutical Biotechnology and Drug Development. Springer Nature Singapore; Singapore: 2024. pp. 387–411.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

