Population Pharmacokinetic Model of Vitamin D3 and Metabolites in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Vitamin D Insufficiency and Deficiency
- PMID: 39596344
- PMCID: PMC11595143
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212279
Population Pharmacokinetic Model of Vitamin D3 and Metabolites in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Vitamin D Insufficiency and Deficiency
Abstract
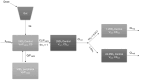
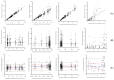
Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are highly prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), and their pharmacokinetics are not well described. The primary study objective was to develop a population pharmacokinetic model of oral cholecalciferol (VitD3) and its three major metabolites, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (25D3), 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25D3), and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (24,25D3), in CKD patients with vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency. CKD subjects (n = 29) were administered one dose of oral VitD3 (5000 I.U.), and nonlinear mixed effects modeling was used to describe the pharmacokinetics of VitD3 and its metabolites. The simultaneous fit of a two-compartment model for VitD3 and a one-compartment model for each metabolite represented the observed data. A proportional error model explained the residual variability for each compound. No assessed covariate significantly affected the pharmacokinetics of VitD3 and metabolites. Visual predictive plots demonstrated the adequate fit of the pharmacokinetic data of VitD3 and metabolites. This is the first reported population pharmacokinetic modeling of VitD3 and metabolites and has the potential to inform targeted dose individualization strategies for therapy in the CKD population. Based on the simulation, doses of 600 International Unit (I.U.)/day to 1000 I.U./day for 6 months are recommended to obtain the target 25D3 concentration of between 30 and 60 ng/mL. These simulation findings could potentially contribute to the development of personalized dosage regimens for vitamin D treatment in patients with CKD.
Keywords: cholecalciferol; chronic kidney disease; population pharmacokinetic model; vitamin D deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Jones G. Vitamin D: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ, USA: 2010. Metabolism and catabolism of vitamin D, its metabolites and clinically relevant analogs; pp. 99–134.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

