The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Xenoestrogens on the Risk of Cancer Development
- PMID: 39596429
- PMCID: PMC11594813
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212363
The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Xenoestrogens on the Risk of Cancer Development
Abstract
Xenoestrogens (XEs) are a group of exogenous substances that may interfere with the functioning of the endocrine system. They may mimic the function of estrogens, and their sources are plants, water or dust, plastic, chemical agents, and some drugs. Thus, people are highly exposed to their actions. Together with the development of industry, the number of XEs in our environment increases. They interact directly with estrogen receptors, disrupting the transmission of cellular signals. It is proven that XEs exhibit clinical application in e.g., menopause hormone therapy, but some studies observed that intense exposure to XEs leads to the progression of various cancers. Moreover, these substances exhibit the ability to cross the placental barrier, therefore, prenatal exposure may disturb fetus development. Due to the wide range of effects resulting from the biological activity of these substances, there is a need for this knowledge to be systematized. This review aims to comprehensively assess the environmental sources of XEs and their role in increasing cancer risk, focusing on current evidence of their biological and pathological impacts.
Keywords: environmental exposure; estrogens; isoflavones; pesticides; xenoestrogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
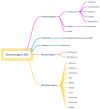
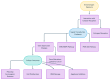
References
-
- Woźniak M., Murias M. Xenoestrogens: Endocrine Disrupting Compounds. Ginekol. Pol. 2008;79:785–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

