Role of Balanced Involvement of the ICOS/ICOSL/Osteopontin Network in Cutaneous Wound Healing
- PMID: 39596455
- PMCID: PMC11594701
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212390
Role of Balanced Involvement of the ICOS/ICOSL/Osteopontin Network in Cutaneous Wound Healing
Abstract
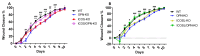
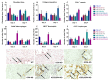
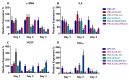
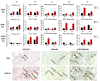
Inducible T-cell costimulator (ICOS, CD278) is a costimulatory receptor primarily expressed by activated T cells. It binds to ICOS ligand (ICOSL, CD275), which is expressed by various immune and non-immune cell types, particularly in inflamed tissues. ICOSL can also bind to osteopontin (OPN), a protein that functions both as a component of the extracellular matrix and as a soluble pro-inflammatory cytokine. Previous studies, including ours, have shown that ICOS and ICOSL play a role in skin wound healing, as mice deficient in either ICOS or ICOSL exhibit delayed healing. The aim of this study was to investigate the involvement of the ICOS/ICOSL/OPN network in skin wound healing by analyzing mice that are single knockouts for ICOS, ICOSL, or OPN, or double knockouts for ICOS/OPN or ICOSL/OPN. Our results showed that wound healing is impaired in all single knockout strains, but not in the two double knockout strains. Cellular and molecular analyses of the wound healing sites revealed that the healing defect in the single knockout strains is associated with reduced neutrophil infiltration and decreased expression of α-SMA (a marker of myofibroblasts), IL-6, TNFα, and VEGF. In contrast, the normalization of wound closure observed in the double knockout strains was primarily linked to increased vessel formation. A local treatment with recombinant ICOS-Fc improved healing in all mouse strains expressing ICOSL, but not in those lacking ICOSL, and led to a local increase in vessel formation and macrophage recruitment, predominantly of the M2 type.
Keywords: ICOS/ICOSL/OPN network; reparative macrophages; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
U.D. is listed among the inventors on the patent WO/2016/189428 “Ligands of B7h receptor in the treatment of osteopenia and osteoporosis” and is one of the founders of an UPO Spinoff (NOVAICOS). U.D. and C.D. listed among the inventors on the patent PCT/IB2019/050154 “Novel anti-tumor therapeutic agents”.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

