The Gut-Heart Axis: Molecular Perspectives and Implications for Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 39596530
- PMCID: PMC11595032
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212465
The Gut-Heart Axis: Molecular Perspectives and Implications for Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Myocardial infarction (MI) remains the leading cause of death globally, imposing a significant burden on healthcare systems and patients. The gut-heart axis, a bidirectional network connecting gut health to cardiovascular outcomes, has recently emerged as a critical factor in MI pathophysiology. Disruptions in this axis, including gut dysbiosis and compromised intestinal barrier integrity, lead to systemic inflammation driven by gut-derived metabolites like lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) and trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), both of which exacerbate MI progression. In contrast, metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) from a balanced microbiota exhibit protective effects against cardiac damage. This review examines the molecular mediators of the gut-heart axis, considering the role of factors like sex-specific hormones, aging, diet, physical activity, and alcohol consumption on gut health and MI outcomes. Additionally, we highlight therapeutic approaches, including dietary interventions, personalized probiotics, and exercise regimens. Addressing the gut-heart axis holds promise for reducing MI risk and improving recovery, positioning it as a novel target in cardiovascular therapy.
Keywords: gut metabolites; gut microbiota; gut–heart axis; intestinal barrier; myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
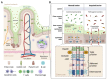

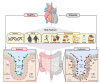
References
-
- Martin S.S., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., Anderson C.A., Arora P., Avery C.L., Baker-Smith C.M., Barone Gibbs B., Beaton A.Z., Boehme A.K., et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2024;149:E347–E913. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yusuf P.S., Hawken S., Ôunpuu S., Dans T., Avezum A., Lanas F., McQueen M., Budaj A., Pais P., Varigos J., et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): Case-control study. Lancet. 2004;364:937–952. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17018-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

