Interaction Between PNPLA3 and SIRT5 Genetic Variants in Association with Liver Fibrosis Severity in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
- PMID: 39596570
- PMCID: PMC11593416
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15111370
Interaction Between PNPLA3 and SIRT5 Genetic Variants in Association with Liver Fibrosis Severity in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
Background/objectives: This study evaluated the association between polymorphisms in the PNPLA3, TM6SF2, HSD17B13, and SIRT5 genes and the severity of fibrosis and steatosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD).
Methods: Fibrosis and steatosis were assessed by MRE and MRI-PDFF, respectively. The polymorphisms were determined by allelic discrimination in blood samples.
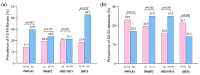
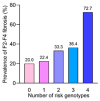
Results: 204 patients aged 57.0 ± 13.5 years were included. Sixty-two (30.4%) patients had significant fibrosis (≥F2). Among F2-F4 fibrosis, the PNPLA3 rs738409 GG genotype was significantly higher than the CC + CG genotypes (44.9% vs. 21.4%, p = 0.001). The SIRT5 rs12216101 GG vs. TT + TG genotypes also exhibited a similar trend (64.3% vs. 27.9%, p = 0.012). In multivariate analysis, the PNPLA3 GG genotype (OR = 3.48, 95%CI: 1.50-8.06; p = 0.004) and SIRT5 rs12216101 GG genotype (OR = 5.43, 95%CI: 1.32-22.33; p = 0.019) were independently associated with F2-F4 fibrosis. Additionally, the proportion of patients with F2-F4 fibrosis significantly increased with the number of combined risk genotypes. Among S2-S3 steatosis, the prevalence of HSD17B13 AG + GG genotypes was higher than that of the AA genotype (37.5% vs. 23.9%, p = 0.048) and independently associated with moderate/severe steatosis in multivariate analysis (OR = 2.26, 95%CI: 1.14-4.49; p = 0.020).
Conclusions: Our data indicate that the PNPLA3 and SIRT5 polymorphisms were independently and additively linked to significant fibrosis, while the HSD17B13 polymorphism was associated with increased steatosis in Thai populations. These data might emphasize the importance of genetic variants in progressive MASLD.
Keywords: HSD17B13 rs6834314; PNPLA3 rs738409; SIRT5 rs12216101; fibrosis; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD); polymorphisms; steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Quek J., Chan K.E., Wong Z.Y., Tan C., Tan B., Lim W.H., Tan D.J.H., Tang A.S.P., Tay P., Xiao J., et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023;8:20–30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00317-X. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

