ANKS6 Variants Underlie Polycystic Kidneys in Prenatal and Neonatal Cases
- PMID: 39596574
- PMCID: PMC11593910
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15111374
ANKS6 Variants Underlie Polycystic Kidneys in Prenatal and Neonatal Cases
Abstract
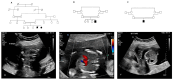
Background: Nephronophthisis (NPHP) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that can cause early-onset kidney failure. ANKS6 plays an important role in early kidney development and encodes a protein that interacts with other proteins within the primary cilium. ANKS6 mutations are known to cause nephronophthisis 16 (NPHP-16). Little is known regarding fetal ultrasound imaging and the antenatal diagnosis of fetuses with ANKS6-associated kidney disease. Here, we report the detection of ANKS6 variants in consanguineous families with polycystic kidney antenatally and in the early stages of life.
Methods: Three unrelated Saudi Arabian patients (two prenatal patients and one neonate) were investigated. These cases were referred to the hospital due to the presence of echogenic kidneys on antenatal scanning. After clinical and phenotypic evaluation, whole-exome sequencing (WES) was performed on the cord and peripheral blood to identify the molecular genetic causes associated with the echogenic kidney phenotypes.
Results: Two homozygous sequence variants were detected in ANKS6. The homozygous missense novel variant ANKS6: c.1159A>C was detected in Families 1 and 2. In the third family, the known homozygous loss-of-function variant ANKS6: c.907+2T>A was detected.
Conclusions: We identified homozygous ANKS6 variants in three families presenting with antenatal polycystic kidney disease. The findings provide an expanded clinical presentation of ANKS6 and emphasize the utility of WES in the diagnosis of echogenic kidneys in prenatal settings.
Keywords: ANKS6; consanguineous; echogenic kidney; nephronophthisis; whole-exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

