RNA Modifications in Pathogenic Viruses: Existence, Mechanism, and Impacts
- PMID: 39597761
- PMCID: PMC11596894
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12112373
RNA Modifications in Pathogenic Viruses: Existence, Mechanism, and Impacts
Abstract
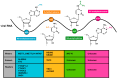
RNA modification is a key posttranscriptional process playing various biological roles, and one which has been reported to exist extensively in cellular RNAs. Interestingly, recent studies have shown that viral RNAs also contain a variety of RNA modifications, which are regulated dynamically by host modification machinery and play critical roles in different stages of the viral life cycle. In this review, we summarize the reports of four typical modifications reported on viral RNAs, including N6-methyladenosine (m6A), 5-methylcytosine (m5C), N4-acetylcytosine (ac4C), and N1-methyladenosine (m1A), describe the molecular mechanisms of these modification processes, and illustrate their impacts on viral replication, pathogenicity, and innate immune responses. Notably, we find that RNA modifications in different viruses share some common features and mechanisms in their generation, regulation, and function, highlighting the potential for viral RNA modifications and the related host machinery to serve as the targets or bases for the development of antiviral therapeutics and vaccines.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine; N1-methyladenosine; N4-acetylcytosine; N6-methyladenosine; RNA modification; viral RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

