Advancements in Virtual Bioequivalence: A Systematic Review of Computational Methods and Regulatory Perspectives in the Pharmaceutical Industry
- PMID: 39598538
- PMCID: PMC11597508
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16111414
Advancements in Virtual Bioequivalence: A Systematic Review of Computational Methods and Regulatory Perspectives in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Abstract
Background/objectives: The rise of virtual bioequivalence studies has transformed the pharmaceutical landscape, enabling more efficient drug development processes. This systematic review aims to explore advancements in physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling, its regulatory implications, and its role in achieving virtual bioequivalence, particularly for complex drug formulations.
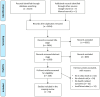
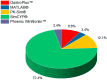
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of clinical trials using computational methods, particularly PBPK modeling, to carry out bioequivalence assessments. Eligibility criteria are emphasized during in silico modeling and pharmacokinetic simulations. Comprehensive literature searches were performed across databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library. A search strategy using key terms and Boolean operators ensured that extensive coverage was achieved. We adhered to the PRISMA guidelines in regard to the study selection, data extraction, and quality assessment, focusing on key characteristics, methodologies, outcomes, and regulatory perspectives from the FDA and EMA.
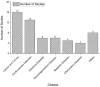
Results: Our findings indicate that PBPK modeling significantly enhances the prediction of pharmacokinetic profiles, optimizing dosing regimens, while minimizing the need for extensive clinical trials. Regulatory agencies have recognized this utility, with the FDA and EMA developing frameworks to integrate in silico methods into drug evaluations. However, challenges such as study heterogeneity and publication bias may limit the generalizability of the results.
Conclusions: This review highlights the critical need for standardized protocols and robust regulatory guidelines to facilitate the integration of virtual bioequivalence methodologies into pharmaceutical practices. By embracing these advancements, the pharmaceutical industry can improve drug development efficiency and patient outcomes, paving the way for innovative therapeutic solutions. Continued research and adaptive regulatory frameworks will be essential in navigating this evolving field.
Keywords: pharmaceutical industry; physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling; regulatory guidelines; virtual bioequivalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sowmya C., Abrar H., Prakaash K. Virtual Bioequivalence in Pharmaceuticals: Current Status and Future Prospects. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2023;15:1–9. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2023v15i5.48589. - DOI
-
- Hirano M., Yamada M., Tanaka T., Koue T., Saito T., Higashimori M., Ochiai H., Yamamoto J., Yaguchi S., Mita S., et al. Surveys/Research Exploring Japanese Phase I Studies in Global Drug Development: Are They Necessary Prior to Joining Global Clinical Trials? Clin. Pharmacol. Drug. Dev. 2021;10:1410–1418. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.1044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

