The Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-1 Is Essential for Dengue Virus Infection
- PMID: 39599807
- PMCID: PMC11599027
- DOI: 10.3390/v16111692
The Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-1 Is Essential for Dengue Virus Infection
Abstract
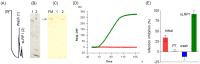
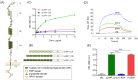
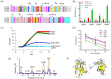
Dengue virus (DENV) causes the most prevalent and rapidly spreading arboviral disease of humans. It enters human cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Numerous cell-surface proteins were proposed as DENV entry factors. Among these, the phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-1 is the only one known to mediate virus internalization. However, several cellular models lacking TIM-1 are permissive to DENV infection, suggesting that other receptors exist. Here, we show that the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1) binds DENV virions by interacting with the DIII of the viral envelope glycoprotein. DENV infection is effectively inhibited by the purified receptor at 5 × 10-8 mol/L, and the interaction of the envelope protein with LRP1 is also blocked by a natural ligand of LRP1. The depletion of LRP1 causes 100-fold lower production of infectious virus than controls. Our results indicate that LRP1 is another DENV receptor, thus becoming an attractive target to evaluate for the development of effective antiviral drugs against DENV.
Keywords: cellular receptor; domain III; virus–receptor interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

