Archived HIV-1 Drug Resistance Mutations: Role of Proviral HIV-1 DNA Genotype for the Management of Virological Responder People Living with HIV
- PMID: 39599811
- PMCID: PMC11599110
- DOI: 10.3390/v16111697
Archived HIV-1 Drug Resistance Mutations: Role of Proviral HIV-1 DNA Genotype for the Management of Virological Responder People Living with HIV
Abstract
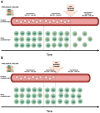
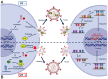
Despite its effectiveness in controlling plasma viremia, antiretroviral therapy (ART) cannot target proviral DNA, which remains an obstacle to HIV-1 eradication. When treatment is interrupted, the reservoirs can act as a source of viral rebound, highlighting the value of proviral DNA as an additional source of information on an individual's overall resistance burden. In cases where the viral load is too low for successful HIV-1 RNA genotyping, HIV-1 DNA can help identify resistance mutations in treated individuals. The absence of treatment history, the need to adjust ART despite undetectable viremia, or the presence of LLV further support the use of genotypic resistance tests (GRTs) on HIV-1 DNA. Conventionally, GRTs have been achieved through Sanger sequencing, but the advances in NGS are leading to an increase in its use, allowing the detection of minority variants present in less than 20% of the viral population. The clinical significance of these mutations remains under debate, with interpretations varying based on context. Additionally, proviral DNA is subject to APOBEC3-induced hypermutation, which can lead to defective, nonviable viral genomes, a factor that must be considered when performing GRTs on HIV-1 DNA.
Keywords: APOBEC; DNA GRT; HIV-1; NGS; Sanger sequencing; reservoir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Colby D.J., Trautmann L., Pinyakorn S., Leyre L., Pagliuzza A., Kroon E., Rolland M., Takata H., Buranapraditkun S., Intasan J., et al. Rapid HIV RNA rebound after antiretroviral treatment interruption in persons durably suppressed in Fiebig I acute HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2018;24:923–926. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0026-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Finzi D., Hermankova M., Pierson T., Carruth L.M., Buck C., Chaisson R.E., Quinn T.C., Chadwick K., Margolick J., Brookmeyer R., et al. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science. 1997;278:1295–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1295. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

