Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Liver Diseases
- PMID: 39599900
- PMCID: PMC11598962
- DOI: 10.3390/v16111785
Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Liver Diseases
Abstract
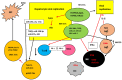
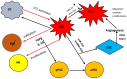
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are bilayer vesicles released by cells in the microenvironment of the liver including parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells. They are the third important mechanism in the communications between cells, besides the secretion of cytokines and chemokines and the direct cell-to-cell contact. The aim of this review is to discuss the important role of EVs in viral liver disease, as there is increasing evidence that the transportation of viral proteins, all types of RNA, and viral particles including complete virions is implicated in the pathogenesis of both viral cirrhosis and viral-related hepatocellular carcinoma. The biogenesis of EVs is discussed and their role in the pathogenesis of viral liver diseases is presented. Their use as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers is also analyzed. Most importantly, the significance of possible novel treatment strategies for liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma is presented, although available data are based on experimental evidence and clinical trials have not been reported.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; hepatitis B; hepatitis C; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver fibrosis; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles: Novel mediator for cell to cell communications in liver pathogenesis.Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Apr;60:115-122. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Mol Aspects Med. 2018. PMID: 29122679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential mechanisms of hepatitis B virus induced liver injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12462-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12462. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25253946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Shuttles of RNA and Their Clinical Significance as Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 11;12(6):902. doi: 10.3390/genes12060902. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Aug;14(8):455-466. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.71. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28634412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intercellular Communication between Hepatic Cells in Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 2;20(9):2180. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092180. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31052525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Other Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 23;26(11):5033. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115033. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Cirrhosis Collaborators The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:245–266. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

