Cardiac remodelling in the era of the recommended four pillars heart failure medical therapy
- PMID: 39600110
- PMCID: PMC11911582
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.15095
Cardiac remodelling in the era of the recommended four pillars heart failure medical therapy
Abstract
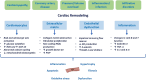
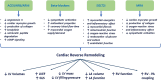
Cardiac remodelling is a key determinant of worse cardiovascular outcome in patients with heart failure (HF) and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). It affects both the left ventricle (LV) structure and function as well as the left atrium (LA) and the right ventricle (RV). Guideline recommended medical therapy for HF, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptors II blockers/angiotensin receptor blocker-neprilysin inhibitors (ACE-I/ARB/ARNI), beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA) and sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), have shown to improve morbidity and mortality in patients with HFrEF. By targeting multiple pathophysiological pathways, foundational HF therapies are supposed to drive their beneficial clinical effects by a direct myocardial effect. Simultaneous initiation of guideline directed medical therapy (GDMT) through a synergistic effect promotes a 'reverse remodelling', leading to a full or partial recovered structure and function by enhancing systemic neurohumoral regulation and energy metabolism, reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis, lowering oxidative stress and inflammation and adverse extracellular matrix deposition. The aim of this review is to describe how these classes of drugs can drive reverse remodelling in the LV, LA and RV and improve prognosis in patients with HFrEF.
Keywords: Cardiac remodelling; Heart failure; Medical therapy.
© 2024 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cohn JN, Ferrari R, Sharpe N. Cardiac remodeling‐‐concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. On behalf of an international forum on cardiac remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000;35:569‐582. - PubMed
-
- Torre‐Amione G, Kapadia S, Benedict C, Oral H, Young JB, Mann DL. Proinflammatory cytokine levels in patients with depressed left ventricular ejection fraction: a report from the studies of left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996;27:1201‐1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

