Relationship between Chinese college students' attitude to physical exercise and psychological capital: the mediating effects of self-control and gender
- PMID: 39600401
- PMCID: PMC11588726
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1443489
Relationship between Chinese college students' attitude to physical exercise and psychological capital: the mediating effects of self-control and gender
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the impact of attitudes toward physical exercise on college students' psychological capital and its mechanism of action, providing new pathways and scientific evidence for enhancing psychological capital among college students.
Methods: A total of 519 college students (mean age: 19.95 ± 1.34) were surveyed using a questionnaire.
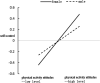
Results: (1) Attitudes toward physical exercise have a significant direct predictive effect on college students' psychological capital; (2) Attitudes toward physical exercise can indirectly predict psychological capital through the mediating role of self-control; (3) The influence of attitudes toward physical exercise on self-control is moderated by gender, with a greater impact on female college students than on male students.
Conclusion: (1) This study investigated the mechanism by which attitudes toward physical exercise influence psychological capital through self-control and gender differences; (2) The study revealed the positive role of psychological capital, with a significant predictive effect of attitudes toward physical exercise on college students' psychological capital (B = 0.46, p < 0.001), and identified the reasons for gender differences, with attitudes toward physical exercise having a stronger promoting effect on self-control in female college students (B = 0.26, t = 3.80, p < 0.001). It provides guiding suggestions for enhancing psychological capital by fostering attitudes toward physical exercise among college students.
Keywords: attitude toward physical exercises; college students; gender; psychological capital; self-control.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Cui, Shen, Luo and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Du X, Chen Y, He Z. A study on physical exercise attitude and behavior of college students in Beijing. J Capital Sports Acad. (2007) 1:70–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-783X.2007.01.018 - DOI
-
- Zhao C. On the significance of physical education to promote the comprehensive development of college students' physical and mental health. Modern Econ Informat. (2016) 27:434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-828X.2016.27.350 - DOI
-
- Zhang H, Guo S. A study of exercise behavior and related knowledge, attitude, and self-efficacy in college students. Chin Behav Med Sci. (2001) 10:133–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6554.2001.02.029 - DOI
-
- Luthans F, Youssef CM. Emerging positive organizational behavior. J Manag. (2007) 33:321–49. doi: 10.1177/0149206307300814 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical