Genome Variability for the Development of Coronary Heart Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 39600715
- PMCID: PMC11590629
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S471606
Genome Variability for the Development of Coronary Heart Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) stand as the foremost global cause of mortality, accounting for 32% of total deaths in 2019, with 85% attributed to heart attacks and strokes. Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) exhibit an elevated susceptibility to coronary heart disease (CHD). In numerous studies, it has been established that genetic polymorphism of genes influences the onset, progression, and complications of coronary heart disease (CHD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The aims of this study are to employ bibliometric analysis methods for mapping the array of research on genome variability concerning the development of coronary heart disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: We derived the data from the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection database and Scopus on January 6, 2023. All publications from 1987 to 2023 are exported in plain text format for WoS-CC and BibTeX format for Scopus, containing bibliographic information, keywords, and citation information. RStudio v.4.1.2 software (RStudio, PBC, Boston, MA, USA) was used for conducting bibliometric analysis.
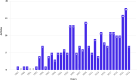
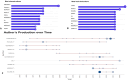
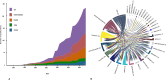
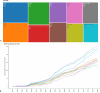
Results: Our analysis of 241 articles published between 1987 and 2023 revealed a consistent increase in research output, especially after 2004, highlighting a growing academic focus on genome variability's role in coronary heart disease (CHD) development among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients. Key contributing journals include The Lancet and Nature Genetics, indicating high-impact interest in this domain. The United States leads in research productivity and collaboration, with China also emerging as a notable contributor in recent years. Prominent authors such as S. Humphries have significantly shaped the field, contributing to a cumulative knowledge base that underscores the role of genetic factors in CHD among T2DM patients.
Discussion: Our findings underscore the value of bibliometric studies in guiding future research directions. This increasing scholarly attention to genome variability in CHD and T2DM may encourage deeper investigation into specific genetic polymorphisms and their mechanistic roles in disease progression. Additionally, these insights can help prioritize collaboration across leading research hubs and potentially drive innovation in therapeutic interventions targeting genetic risk factors in CHD and T2DM. Future research could build on these trends by focusing on comparative studies across populations, advancing precision medicine approaches for at-risk individuals with T2DM.
Keywords: Bibliometric Analysis; Coronary Heart Disease; Genome Variability; Research Hotspots; Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
© 2024 Bekenova et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Nazira B Bekenova and Tamara A Vochshenkova are co-first authors for this study. Amin Tamadon was employed by PerciaVista R&D Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ. IDF Diabetes ATLAS. IDF DIABETES ATLAS. IDF Diabetes Atlas. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation © International Diabetes Federation; 2021.
-
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) 2021 Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...). Accessed November 19, 2024
-
- Zarkasi KA, Abdul Murad NA, Ahmad N, Jamal R, Abdullah N. Coronary Heart Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: genetic Factors and Their Mechanisms, Gene-Gene, and Gene-Environment Interactions in the Asian Populations. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(2). doi: 10.3390/ijerph19020647 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

