Lipin1 as a therapeutic target for respiratory insufficiency of duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 39600918
- PMCID: PMC11588688
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1477976
Lipin1 as a therapeutic target for respiratory insufficiency of duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
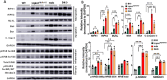
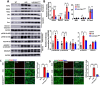
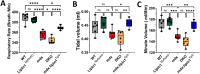
In Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), diaphragm muscle dysfunction results in respiratory insufficiency which is a leading cause of death in patients. Mutations to the dystrophin gene result in myocyte membrane instability, contributing to the structural deterioration of the diaphragm muscle tissues. With previous works suggesting the importance of lipin1 for maintaining skeletal muscle membrane integrity, we explored the roles of lipin1 in the dystrophic diaphragm. We found that the protein expression levels of lipin1 were reduced by 60% in the dystrophic diaphragm. While further knockdown of lipin1 in the dystrophic diaphragm leads to increased necroptosis, restoration of lipin1 in the dystrophic diaphragm results in reduced inflammation and fibrosis, decreased myofiber death, and improved respiratory function. Our results demonstrated that lipin1 restoration improved respiratory function by enhancing membrane integrity and suggested that lipin1 could be a potential therapeutic target for preventing respiratory insufficiency and respiratory failure in DMD. Continued investigation is required to better understand the mechanisms behind these findings, and to determine the role of lipin1 in maintaining muscle membrane stability.
Keywords: DMD; diaphragm; dystrophin; lipin1; membrane integrity; muscular dystrophy; skeletal muscle; therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2024 Brown, Morris, Kamau, Rakoczy, Finck, Wyatt and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Acharyya S., Villalta S. A., Bakkar N., Bupha-Intr T., Janssen P. M., Carathers M., et al. (2007). Interplay of IKK/NF-kappaB signaling in macrophages and myofibers promotes muscle degeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 117 (4), 889–901. 10.1172/JCI30556 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

