Liver fibrotic burden across the spectrum of hypothyroidism
- PMID: 39601802
- PMCID: PMC11880098
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-024-02184-x
Liver fibrotic burden across the spectrum of hypothyroidism
Abstract
Background: Data regarding the prevalence of hepatic fibrotic burden across the spectrum of hypothyroidism are scarce. Hence, we aimed to evaluate the prevalence of liver fibrotic burden across the spectrum of hypothyroidism.
Methods: 30,091 individuals who attended a Health Management Centre between 2019 and 2021 were cross-sectionally analyzed. Participants were categorized as having strict-normal thyroid function, low-normal thyroid function, subclinical hypothyroidism, and overt hypothyroidism. Hepatic fibrosis was assessed by vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE). Significant and advanced fibrosis were defined as liver stiffness measurement in VCTE of 8.1-9.6 and 9.7-13.5 kPa, respectively.
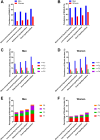
Results: Among both men and women, low-normal thyroid function group, subclinical hypothyroidism group, and overt hypothyroidism group all have more liver fibrosis present, including mild fibrosis, significant fibrosis, advanced fibrosis, and cirrhosis, than the strict-normal thyroid function group. The low-normal thyroid function group have the similar liver fibrotic burden to the subclinical hypothyroidism group. The highest liver fibrotic burden was noted in the overt hypothyroidism group. Both significant and advanced liver fibrosis were significantly associated with low-normal thyroid function, subclinical hypothyroidism, and overt hypothyroidism in both men and women.
Conclusions: Liver fibrotic burden are highly prevalent in subjects with overt hypothyroidism. Moreover, fibrotic burden increased across the spectrum of hypothyroidism even within the low normal thyroid function. These results suggested that screening for liver fibrosis in patients with hypothyroidism is necessary.
Keywords: Advanced fibrosis; Hypothyroidism; Liver stiffness; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Significant fibrosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

