Kidney lipid metabolism: impact on pediatric kidney diseases and modulation by early-life nutrition
- PMID: 39601825
- PMCID: PMC12031794
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-024-06595-z
Kidney lipid metabolism: impact on pediatric kidney diseases and modulation by early-life nutrition
Abstract
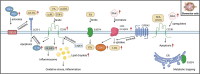
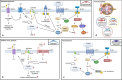
Our review summarizes and evaluates the current state of knowledge on lipid metabolism in relation to the pathomechanisms of kidney disease with a focus on common pediatric kidney diseases. In addition, we discuss how nutrition in early childhood can alter kidney development and permanently shape kidney lipid and protein metabolism, which in turn affects kidney health and disease throughout life. Comprehensive integrated lipidomics and proteomics network analyses are becoming increasingly available and offer exciting new insights into metabolic signatures. Lipid accumulation, lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, and dysregulated pro-inflammatory lipid mediator signaling have been identified as important mechanisms influencing the progression of minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy, diabetic kidney disease, and acute kidney injury. We outline key features of metabolic homeostasis and lipid metabolic physiology in renal cells and discuss pathophysiological aspects in the pediatric context. On the one hand, special vulnerabilities such as reduced antioxidant capacity in neonates must be considered. On the other hand, there is a unique window of opportunity during kidney development, as nutrition in early life influences the composition of cellular phospholipid membranes in the growing kidney and thus affects local signaling pathways far beyond the growth phase.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Children; Early-life nutrition; Kidney lipid metabolism; Lipidomics; Oxidative stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ehren R, Benz MR, Brinkkötter PT, Dötsch J, Eberl WR, Gellermann J, Hoyer PF, Jordans I, Kamrath C, Kemper MJ, Latta K, Müller D, Oh J, Tönshoff B, Weber S, Weber LT (2021) Pediatric idiopathic steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: diagnosis and therapy -short version of the updated German best practice guideline (S2e) - AWMF register no. 166–001, 6/2020. Pediatr Nephrol 36:2971–2985 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomas ME, Schreiner GF (1993) Contribution of proteinuria to progressive renal injury: consequences of tubular uptake of fatty acid bearing albumin. Am J Nephrol 13:385–398 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

