Potential Effect of Etoricoxib in Reducing Inflammation in Methotrexate-Induced Pulmonary Injury in Rats: Role of Oxidative Stress and the TLR4/p38-MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 39602008
- PMCID: PMC12336082
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-024-02198-w
Potential Effect of Etoricoxib in Reducing Inflammation in Methotrexate-Induced Pulmonary Injury in Rats: Role of Oxidative Stress and the TLR4/p38-MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
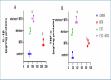
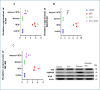
Numerous chemotherapeutic medications can have hazardous effects on the lungs, which can result in severe lung diseases. Methotrexate (MTX) is prescribed for cancer and inflammation-related disorders; nevertheless, it is exceptionally highly toxic and has multiple kinds of adverse reactions, including pulmonary injury. Our work was designed to demonstrate the ability of etoricoxib (ETO) to mitigate MTX-induced lung injury in experimental animals. Adult male Wistar rats were separated into four groups. The first group consisted of healthy controls that received carboxymethyl cellulose (1 ml/day, p.o.), the second group received a single dose of MTX (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.), the third group received ETO (10 mg/kg/day, p.o.) for three weeks, and the fourth group first received a single MTX (20 mg/kg, i.p.) and then was treated with ETO for three weeks. Concomitant treatment with ETO and MTX improved the histological structure of the lung tissue. It significantly altered the levels of oxidant/antioxidant markers, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), reduced glutathione (GSH), and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2), in favor of antioxidants. Moreover, ETO can normalize the proinflammatory cascade, which includes tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). At the molecular level, ETO downregulated the protein expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) in inflamed rat lungs. In conclusion, our findings indicate that oral administration of ETO ameliorates MTX-induced lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB and TLR4/p38-MAPK inflammatory signaling pathways.
Keywords: ETO; Inflammation; MTX; NF-κβ; Oxidative stress; Pulmonary toxicity; TLR-4.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selenium protected NMRI mice against methotrexate induced testicular injury : Selenium effectiveness in methotrexate treated testis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 8;15(1):24448. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09728-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40629028 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine alleviates oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial apoptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced bovine endometrial epithelial cells by activating nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting TLR4-mapk/NF-κb and Caspase-3 pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 15;1003:177986. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177986. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40706972
-
[Mechanisms of Neiyiting Decoction in Preventing Postoperative Recurrence of Endometriosis by Inhibiting Macrophage M1 Polarization Through the TREM1/TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 20;56(2):371-381. doi: 10.12182/20250360601. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40599271 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of immunomodulatory properties of naringenin on the inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress in autoimmune disease models: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical evidence.Inflamm Res. 2022 Nov;71(10-11):1127-1142. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01599-7. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35804246
Cited by
-
Modulation of AMPK by esomeprazole and canagliflozin mitigates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity: involvement of MAPK/JNK/ERK, JAK1/STAT3, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10901-10919. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03908-3. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40055205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Limper, A.H. 2004. Chemotherapy-induced lung disease. Clinics in Chest Medicine 25 (1): 53–64. - PubMed
-
- Alfwuaires, M.A. 2022. Galangin mitigates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in a rat model of methotrexate hepatotoxicity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International 29 (14): 20279–20288. - PubMed
-
- Ohbayashi, M., et al. 2014. Involvement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in methotrexate-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Journal of Toxicological Sciences 39 (2): 319–330. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

