Genetic evidence against involvement of TRPC proteins in SOCE, ROCE, and CRAC channel function
- PMID: 39602257
- PMCID: PMC11626178
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2411389121
Genetic evidence against involvement of TRPC proteins in SOCE, ROCE, and CRAC channel function
Abstract
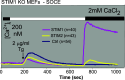
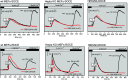
Using genetically engineered mice and cell lines derived from genetically engineered mice we show that depletion of ER delimited Ca2+ stores activates heteromeric Ca2+ entry (SOCE) channels formed obligatorily, but not exclusively by Orai1 molecules. Comparison of Orai-dependent Ca2+ entries revealed Orai1 to be dominant when compared to Orai2 and Orai3. Unexpectedly, we found that store-depletion-activated Ca2+ entry does not depend obligatorily on functionally intact TRPC molecules, as SOCE monitored with the Fura2 Ca2+ reporter dye is unaffected in cells in which all seven TRPC coding genes have been structurally and functionally inactivated. Unexpectedly as well, we found that TRPC-independent Gq-coupled receptor-operated Ca2+ entry (ROCE) also depends on Orai1. Biophysical measurements of Ca2+ release activated Ca2+ currents (Icrac) are likewise unaffected by ablation of all seven TRPC genes. We refer to mice and cells carrying the seven-fold disruption of TRPC genes as TRPC heptaKO mice and cells. TRPC heptaKO mice are fertile allowing the creation of a new homozygous inbred strain.
Keywords: Orai; ROCE; SOCE; TRPC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures










References
-
- Liao Y., Abramowitz J., Birnbaumer L., The TRPC family of TRP channels: Roles inferred (mostly) from knockout mice and relationship to ORAI proteins. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 223, 1055–1075 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

