Treatment patterns and outcomes in follicular lymphoma with POD24: an analysis from the LEO Consortium
- PMID: 39602301
- PMCID: PMC11909426
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014053
Treatment patterns and outcomes in follicular lymphoma with POD24: an analysis from the LEO Consortium
Abstract
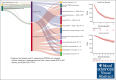
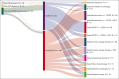
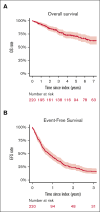
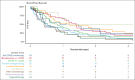
Progression of disease within 24 months of initial immunochemotherapy (POD24) is a negative prognostic factor for patients with follicular lymphoma (FL). There is no standard treatment after POD24. Assembling an academic-based cohort from the Lymphoma Epidemiology of Outcomes Consortium for Real World Evidence, we evaluated patterns of care and outcomes for 220 patients with FL with POD24 and retained FL histology. Therapy after POD24 was heterogeneous, with no treatment category accounting for >25% of the total. Among patients initially treated with bendamustine-rituximab, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone (R-CHOP) was the predominant second-line choice (48%). Among patients initially treated with R-CHOP, aggressive salvage therapy was the predominant second-line choice (38%). Overall response rate to therapy after POD24 was 64% (95% confidence interval [CI], 56-70); complete response rate was 39% (95% CI, 32-46). The median event-free survival for therapy after POD24 was 9.8 months (95% CI, 7.3-12.1); 5-year overall survival (OS) was 71% (95% CI, 65-78). OS was inferior for patients aged >70 years (hazard ratio [HR], 2.31; 95% CI, 1.27-4.20) and those with high-risk FL International Prognostic Index scores at diagnosis (HR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.23-3.60). No treatment category stood out with more favorable results. Cause of death was predominantly lymphoma related. Patients with follicular histology at their POD24 event had a low cumulative incidence of transformation (1.1% at 5 years). Our study is among the largest cohorts describing contemporary patterns of care for patients with POD24, providing a focused data set useful for interpreting and designing prospective clinical trials in this population.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: Y.W. reports research funding from LOXO Oncology, Novartis, MorphoSys, Innocare, Incyte, Genentech, Eli Lilly, and Genmab; membership on an entity's board of directors or advisory committees for LOXO Oncology, TG Therapeutics, Innocare, Incyte, Eli Lilly, BeiGene, Kite, Janssen, and AstraZeneca; consultancy fees from Innocare and AbbVie; and honoraria from Kite. L.J.N. reports honoraria from Gilead Sciences/Kite Pharma, AstraZeneca, Regeneron, Genentech, Inc, Genmab, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Takeda, AbbVie, Daiichi Sankyo, DeNovo, Caribou Biosciences, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, and ADC Therapeutics; and research funding from Gilead Sciences/Kite Pharma, Genentech, Inc, Genmab, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, Caribou Biosciences, and Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene. P.M. reports consultancy fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Epizyme, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Pepromene, and Daiichi Sankyo. I.S.L. reports membership on an entity's board of directors or advisory committees for Lymphoma Research Foundation; research funding from the National Cancer Institute; honoraria from Adaptive; current employment with University of Miami; and consultancy fees from BeiGene. J.R.C. reports research funding from Genmab, Bristol Myers Squibb, NanoString, and Genentech; membership on an entity's board of directors or advisory committees for Bristol Myers Squibb; and safety monitoring committee fees from Protagonist. C.R.F. reports consultancy fees from BeiGene, N-Power Medicine, Genentech Roche, SeaGen, Bayer, AbbVie, Genmab, Gilead, Spectrum, Pharmacyclics Jansen, Karyopharm, Denovo Biopharma, and Foresight Diagnostics; research funding from 4D, MorphoSys, Genentech Roche, Acerta, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Bayer, AbbVie, Gilead, Pfizer, Nektar, Pharmacyclics, Sanofi, Takeda, Guardant, Iovance, Kite, Celgene, Novartis, Ziopharm, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group, National Cancer Institute, V Foundation, Adaptimmune, Allogene, TG Therapeutics, Xencor, CPRIT Scholar in Cancer Research, Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, Amgen, and Cellectis; and is a current holder of stock options in a privately held company in N-Power Medicine and Foresight Diagnostics. C.C. reports research funding from SecuraBio, GenMab, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Verastem, and Genentech; consultancy fees from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Genentech; and leadership role fees from Follicular Lymphoma Foundation. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(6):443–459. - PubMed
-
- Mounier M, Bossard N, Remontet L, et al. Changes in dynamics of excess mortality rates and net survival after diagnosis of follicular lymphoma or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: comparison between European population-based data (EUROCARE-5) Lancet Haematol. 2015;2(11):e481–e491. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials