Temporal Dynamics of Plasma Neurofilament Light in Blood Donors With Preclinical Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 39602675
- PMCID: PMC11616971
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200335
Temporal Dynamics of Plasma Neurofilament Light in Blood Donors With Preclinical Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a CNS disease, characterized by demyelination, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. Recent advances in technology allow measurement of the axonal damage marker neurofilament light chain in peripheral blood. Two studies have shown that patients with MS have elevated neurofilament light levels before their first symptom, but longitudinal studies are lacking. We aimed to investigate the intraindividual neurofilament light dynamics during the presymptomatic phase of MS.
Methods: The Danish Blood Donor Study (DBDS) has stored plasma samples from blood donors for more than 10 years. We identified DBDS participants, who had subsequently been diagnosed with MS, and included all samples donated before their first demyelinating symptom (median 5.00 samples per case). As controls, we included 2 healthy donors per case. Plasma levels of neurofilament light were measured and compared with quality-of-life data. We used a Bayesian approach to derive estimates for the percentage of cases with presymptomatic increased neurofilament light levels.
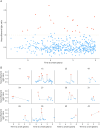
Results: We observed that 12 (17%, 95% CI 9%-28%) of 69 presymptomatic MS donors had intermittently increased neurofilament light levels preclinically. Increased levels were present up to 9 years before clinical onset, also in primary progressive MS. Healthy donors and presymptomatic MS donors with and without increased neurofilament light levels reported equally high physical and mental well-being. Model-based estimates suggested that 55% of cases (95% credible interval [28%-87%]) had experienced increased presymptomatic neurofilament light levels.
Discussion: Patients with MS periodically sustain axonal injury up to 9 years before clinical onset, even in primary progressive disease. This most likely represents asymptomatic disease activity. Some or even all patients are affected by this intermittent axonal injury, prompting the need for further studies of the presymptomatic phase in relation to prognosis and as a therapeutic window of opportunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
