Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges, advances, and clinical implications
- PMID: 39604328
- PMCID: PMC11925447
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0541
Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges, advances, and clinical implications
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive primary liver malignancy often diagnosed at an advanced stage, resulting in a poor prognosis. Accurate risk stratification and early detection of HCC are critical unmet needs for improving outcomes. Several blood-based biomarkers and imaging tests are available for early detection, prediction, and monitoring of HCC. However, serum protein biomarkers such as alpha-fetoprotein have shown relatively low sensitivity, leading to inaccurate performance. Imaging studies also face limitations related to suboptimal accuracy, high cost, and limited implementation. Recently, liquid biopsy techniques have gained attention for addressing these unmet needs. Liquid biopsy is non-invasive and provides more objective readouts, requiring less reliance on healthcare professional's skills compared to imaging. Circulating tumor cells, cell-free DNA, and extracellular vesicles are targeted in liquid biopsies as novel biomarkers for HCC. Despite their potential, there are debates regarding the role of these novel biomarkers in the HCC care continuum. This review article aims to discuss the technical challenges, recent technical advancements, advantages and disadvantages of these liquid biopsies, as well as their current clinical application and future directions of liquid biopsy in HCC.
Keywords: Biomarker; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ju Dong Yang provides a consulting service for Fuji-Film Medical Sciences, Exact Sciences, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Exelixis, and Merck. Dr. Yazhen Zhu is a co-founder and shareholder in Eximius Diagnostics Corp.
Following the management plan provide by UCLA Conflict of Interest Review Committee, Dr. Hsian-Rong Tseng would like to disclose that (1) he has a financial interest in CytoLumina Technologies Corp. and Pulsar Therapeutics Corp., and (2) the UC Regents have licensed intellectual properties invented by Dr. Tseng to CytoLumina and Pulsar. Dr. Vatche Agopian provides a consulting service for Merck, Eximius Diagnostics Corp, and Early Diagnostics Corp.
Figures

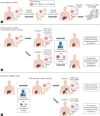
References
-
- Poulet G, Massias J, Taly V. Liquid biopsy: general concepts. Acta Cytol. 2019;63:449–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA273925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01EB026421/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA255727/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA259534/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA280444/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA273925/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA246304/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA255727/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA253651-04S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- K08CA259534/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 EB026421/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA253651/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA277530/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA271887/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R44CA288163/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R44 CA288163/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA277530/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA253651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA246304/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA280444/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

