Genome-wide identification of TaeGRASs responsive to biotic stresses and functional analysis of TaeSCL6 in wheat resistance to powdery mildew
- PMID: 39604842
- PMCID: PMC11603631
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-11041-3
Genome-wide identification of TaeGRASs responsive to biotic stresses and functional analysis of TaeSCL6 in wheat resistance to powdery mildew
Abstract
Background: Powdery mildew is a devastating fungal disease that poses a significant threat to wheat yield and quality worldwide. Identifying resistance genes is highly advantageous for the molecular breeding of resistant cultivars. GRAS proteins are important transcription factors that regulate plant development and stress responses. Nonetheless, their roles in wheat-pathogen interactions remain poorly understood.
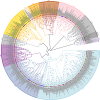
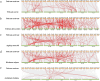
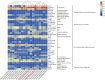
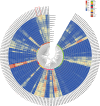
Results: In this study, we used bioinformatics tools to identify and analyze wheat GRAS family genes responsive to biotic stresses and elucidated the function of TaeSCL6 within this family. A total of 179 GRAS genes in wheat were unevenly distributed on 7 chromosomes, and classified into 12 subfamilies based on phylogenetic relationship analysis. Gene duplication analysis revealed 13 pairs of tandem repeats and 142 pairs of segmental duplications, which may account for the rapid expansion of the wheat GRAS family. Expression pattern analysis revealed that 75% of the expressed TaeGRAS genes are responsive to biotic stresses. Few studies have focused on the roles of HAM subfamily genes. Consequently, we concentrated our analysis on the members of the HAM subfamily. Fourteen motifs were identified in the HAM family proteins from both Triticeae species and Arabidopsis, indicating that these motifs were highly conserved during evolution. Promoter analysis indicated that the promoters of HAM genes contain several cis-regulatory elements associated with hormone response, stress response, light response, and growth and development. Both qRT-PCR and RNA-seq data analyses demonstrated that TaeSCL6 responds to Blumeria graminis infection. Therefore, we investigated the role of TaeSCL6 in regulating wheat resistance via RNA interference and barley stripe mosaic virus induced gene silencing. Wheat plants with silenced TaeSCL6 exhibited increased susceptibility to powdery mildew.
Conclusions: In summary, this study not only validates the positive role of TaeSCL6 in wheat resistance to powdery mildew, but also provides candidate gene resources for future breeding of disease-resistance wheat cultivars.
Keywords: GRAS; Powdery mildew; RNA interference; TaeSCL6; Virus-induced gene silencing; Wheat.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Wheat Mediator Subunit TaMED25 Interacts with the Transcription Factor TaEIL1 to Negatively Regulate Disease Resistance against Powdery Mildew.Plant Physiol. 2016 Mar;170(3):1799-816. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01784. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26813794 Free PMC article.
-
TaEDS1 genes positively regulate resistance to powdery mildew in wheat.Plant Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;96(6):607-625. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0718-9. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Plant Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29582247
-
Large-Scale Cloning and Comparative Analysis of TaNAC Genes in Response to Stripe Rust and Powdery Mildew in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 12;11(9):1073. doi: 10.3390/genes11091073. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32932603 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of genes related to resistance against powdery mildew in wheat-Thinopyrum alien addition disomic line germplasm SN6306.Gene. 2016 Sep 15;590(1):5-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27265028 Review.
-
CRISPR-mediated genome editing of wheat for enhancing disease resistance.Front Genome Ed. 2025 Feb 25;7:1542487. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2025.1542487. eCollection 2025. Front Genome Ed. 2025. PMID: 40070798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRAS gene family and their expression profiles under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses in Amorphophallus konjac.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 8;26(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11777-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40629278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohan N, Jhandai S, Bhadu S, Sharma L, Kaur T, Saharan V, Pal A. Acclimation response and management strategies to combat heat stress in wheat for sustainable agriculture: a state-of-the-art review. Plant Sci. 2023;336:111834. - PubMed
-
- Singh A, Singhal C, Sharma AK, Khurana P. Identification of universal stress proteins in wheat and functional characterization during abiotic stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2023;42(9):1487–501. - PubMed
-
- Singh RP, Singh PK, Rutkoski J, Hodson DP, He X, Jørgensen LN, Hovmøller MS, Huerta-Espino J. Disease impact on wheat yield potential and prospects of genetic control. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2016;54:303–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

