Prehospital telemedicine support for urban stroke care: Analysis of current state of care and conceptualization
- PMID: 39604854
- PMCID: PMC11600966
- DOI: 10.1186/s12873-024-01142-3
Prehospital telemedicine support for urban stroke care: Analysis of current state of care and conceptualization
Abstract
Background: The reduction of processing times in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke is of outstanding importance. Our objective is to analyze the acute stroke care chain from onset to treatment in a city in Germany comprising three stroke units. Additionally, we discuss solutions for detected treatment delays.
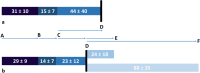
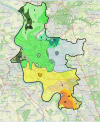
Methods: We conducted an in-depth analysis of acute stroke care processing times across three local stroke centers in Düsseldorf among all emergency services transportations for suspected stroke. Isochrone mapping was performed to identify areas with prolonged transportation times.
Results: Among the 1,714 transportations, 943 patients had confirmed strokes. Prehospital care constituted 58% of total emergency care time until imaging. Patients with confirmed stroke had reduced in-hospital times while patients receiving treatment experienced faster in-hospital times. Isochrone mapping revealed disparities in transportation times within the city.
Conclusions: In conclusion, we identified confirmation of stroke symptoms as pre- and in-hospital and treatment eligibility as in-hospital process accelerators in stroke care. We propose the introduction of an in-ambulance video consulting model to accelerate contact to stroke-experts and accelerate processing times for patients eligible for treatment. Furthermore, we discuss the combination of in-ambulance video consulting with imaging and starting treatment outside traditional stroke centers, followed by transportation to a stroke center during thrombolysis, which might further accelerate treatment in specific cases.
Keywords: Cost efficiency; Models of care; Outcome; Stroke.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Both the approval of the study and the waiver of written informed consent were granted by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the Heinrich Heine University Duesseldorf, Moorenstraße 5, 40225 Duesseldorf (ID: 2021–1494). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(24):2285–95. - PubMed
-
- Kim JT, Fonarow GC, Smith EE, Reeves MJ, Navalkele DD, Grotta JC, et al. Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator in the golden hour and the shape of the 4.5-hour time-benefit curve in the national United States get with the guidelines-stroke population. Circulation. 2017;135(2):128–39. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

