A randomized trial of MONOFIX® vs. V-loc™ for resection bed suture during robotic partial nephrectomy
- PMID: 39604891
- PMCID: PMC11600744
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-13213-6
A randomized trial of MONOFIX® vs. V-loc™ for resection bed suture during robotic partial nephrectomy
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Monofix®-PDO compared to V-Loc™ for tumor bed suturing during robotic-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy (RAPN).
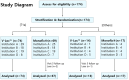
Methods: A randomized, controlled, multicenter, single-blinded trial was conducted across four tertiary institutions. Patients with T1-2 stage renal masses scheduled for RAPN were enrolled. The exclusion criteria included patients not deemed in need of bed suturing, those with a history of prior chemotherapy or immunotherapy, and those with severe systemic diseases or high bleeding tendencies. A total of 174 patients participated and were subjected to permuted block randomization (T1a vs. others), resulting in 88 patients in the V-Loc™ group and 86 in the Monofix®-PDO group. The primary outcome was the resection bed suture time. The secondary outcomes were total suture use time, warm ischemia time, console time (for efficacy), estimated blood loss, hemoglobin change, and 90-day treatment-related adverse events (for safety). All patients were scheduled for follow-up visits for up to three months postoperatively.
Results: The primary outcome, resection bed suture time, did not significantly differ between the V-Loc™ and Monofix®-PDO groups (4.8 ± 2.6 vs. 4.5 ± 2.6 min, p = 0.531). Secondary outcomes, including total suture used time (5.3 ± 2.8 vs. 4.8 ± 2.6 min, p = 0.289) and warm ischemic time (15.6 ± 5.5 vs. 15.4 ± 5.4 min, p = 0.834), were comparable between the two groups. In terms of safety outcomes, changes in serum hemoglobin levels did not show significant differences on postoperative days 1, 3, and 14 (P = 0.537, 0.353, and 0.840, respectively). No device-related adverse events were observed during the 90-day follow-up period in either group.
Conclusions: Monofix®-PDO demonstrated non-inferior to V-Loc in terms of both safety and efficacy in patients undergoing RAPN. This trial is registered on cris.nih.go.kr as KCT0006809 (Registration date: 02/19/2021).
Keywords: Barbed suture; Bed suture time; Monofix; Partial nephrectomy; V-Loc.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The trial protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea (2007-008-1140). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. The study was performed in accordance with the applicable laws and regulations, good clinical practice, and ethical principles as described in the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- F DIM, Bravi CA, Piramide F, Dell’oglio P, Andras RDEG, Turri I, Covas Moschovas F, Paciotti M, Grosso M. How to tailor renorrhaphy technique during robot-assisted partial nephrectomy. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2024;76(2):263–6. - PubMed
-
- Bertolo R, Campi R, Klatte T, Kriegmair MC, Mir MC, Ouzaid I, Salagierski M, Bhayani S, Gill I, Kaouk J, et al. Suture techniques during laparoscopic and robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: a systematic review and quantitative synthesis of peri-operative outcomes. BJU Int. 2019;123(6):923–46. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical