Mechanism of jianxin granules in the treatment of heart failure based on proteomics and metabolomics
- PMID: 39605071
- PMCID: PMC11604013
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-01009-6
Mechanism of jianxin granules in the treatment of heart failure based on proteomics and metabolomics
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is associated with high mortality and rehospitalization rates, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic approaches. Jianxin (JX) granules, a Traditional Chinese Medicine formulation, have been patented for the treatment of HF. However, the specific therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of JX granules have not been fully elucidated. This study aimed at investigating the effects and mechanism of JX granules in the treatment of HF based on proteomics and metabolomic profiling.
Methods: HF model was established in rats by ligation of left coronary artery. The successfully modeled rats were randomly divided into three groups: the model group, the JX granules group, and Sacubitril/Valsartan (S/V) group. Four weeks after treatment, left ventricular (LV) function was evaluated via echocardiography. LV fibrosis and apoptosis were examined through histological analyses, while mitochondrial morphology was assessed using transmission electron microscopy. Quantitative assessment of oxidative stress was also conducted. Proteomics was used to identify the differentially expressed proteins and potential pathways. Metabolomics was utilized to elucidate the variations in metabolism. Then western blotting and in vitro analyses were performed.
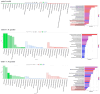
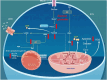
Results: A rat model of HF was established, evidenced by a decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), stroke volume (SV), and left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS), alongside diminished adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content, elevated oxidative stress, augmented apoptosis, and disrupted pyruvate metabolism. Treatment with JX granules ameliorated these effects, improving systolic function, reducing ventricular chamber size, and increasing LVEF, SV, and LVFS, as assessed by echocardiography. Additionally, JX granules attenuated cardiac fibrosis and improved mitochondrial structure, as evidenced by less vacuolation and clearer mitochondrial cristae, when compared to the model group. The treatment also regulated apoptosis-related protein expression, partially reversing the increase in cleaved Caspase-9, cleaved Caspase-3, and Bax and the suppression of Bcl-2 observed in the heart failure rats. All of these effects were similar to S/V. Proteomic and metabolomic analyses identified key differential genes, such as triosephosphate isomerase 1 (TPI1), lactate dehydrogenase B (LDHB), pyruvate kinase M (PKM), protein kinase B (Akt), Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Beta (PDHB) and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), as well as vital pathways including carbon metabolism, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, pyruvate metabolism, and HIF-1α signaling pathway. Moreover, JX granules mitigated oxidative stress, inhibited apoptosis, and activated Akt in H9c2 cells exposed to angiotensin II, which could be reversed by the PI3K inhibitor LY294002.
Conclusion: JX granules improve HF in parallel to the efficacy of S/V, at least in part, through enhancing pyruvate metabolism, inhibiting oxidative stress and activating PI3K/Akt pathway.
Keywords: Heart failure; JX granules; Metabolomics; PI3K/Akt signaling pathway; Proteomics; Pyruvate metabolism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests related to this study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figures








References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

