This is a preprint.
Quantification of subcellular RNA localization through direct detection of RNA oxidation
- PMID: 39605352
- PMCID: PMC11601319
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.12.623278
Quantification of subcellular RNA localization through direct detection of RNA oxidation
Update in
-
Quantification of subcellular RNA localization through direct detection of RNA oxidation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 27;53(5):gkaf139. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf139. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40037712 Free PMC article.
Abstract
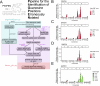
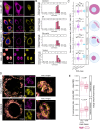
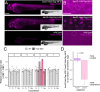
Across cell types and organisms, thousands of RNAs display asymmetric subcellular distributions. The study of this process often requires quantifying abundances of specific RNAs at precise subcellular locations. To analyze subcellular transcriptomes, multiple proximity-based techniques have been developed in which RNAs near a localized bait protein are specifically labeled, facilitating their biotinylation and purification. However, these complex methods are often laborious and require expensive enrichment reagents. To streamline the analysis of localized RNA populations, we developed Oxidation-Induced Nucleotide Conversion sequencing (OINC-seq). In OINC-seq, RNAs near a genetically encoded, localized bait protein are specifically oxidized in a photo-controllable manner. These oxidation events are then directly detected and quantified using high-throughput sequencing and our software package, PIGPEN, without the need for biotin-mediated enrichment. We demonstrate that OINC-seq can induce and quantify RNA oxidation with high specificity in a dose- and light-dependent manner. We further show the spatial specificity of OINC-seq by using it to quantify subcellular transcriptomes associated with the cytoplasm, ER, nucleus, and the inner and outer membranes of mitochondria. Finally, using transgenic zebrafish, we demonstrate that OINC-seq allows proximity-mediated RNA labeling in live animals. In sum, OINC-seq together with PIGPEN provide an accessible workflow for the analysis of localized RNAs across different biological systems.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Long R.M., Singer R.H., Meng X., Gonzalez I., Nasmyth K. and Jansen R.P. (1997) Mating type switching in yeast controlled by asymmetric localization of ASH1 mRNA. Science, 277, 383–387. - PubMed
-
- Lécuyer E., Yoshida H., Parthasarathy N., Alm C., Babak T., Cerovina T., Hughes T.R., Tomancak P. and Krause H.M. (2007) Global analysis of mRNA localization reveals a prominent role in organizing cellular architecture and function. Cell, 131, 174–187. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
