This is a preprint.
UV-B-Induced DNA Repair Mechanisms and Their Effects on Mutagenesis and Culturability in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 39605428
- PMCID: PMC11601333
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.14.623584
UV-B-Induced DNA Repair Mechanisms and Their Effects on Mutagenesis and Culturability in Escherichia coli
Abstract
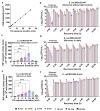
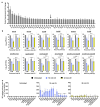
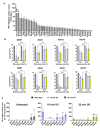
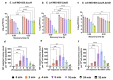
Ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation, intensified by ozone depletion, induces DNA damage and promotes mutagenesis, shaping evolution. While UV-induced SOS responses are well characterized in bacteria, the cellular consequences of prolonged UV-B exposure remain less clear. Prolonged UV-B exposure disrupts translation and RecA-mediated SOS induction without major changes in membrane permeability or reactive oxygen species. This impairs mutagenesis and induces a reversible loss of culturability. Genetic analysis reveals both redundant and differential roles for DNA repair pathways: homologous recombination (RecA, RecB), nucleotide excision repair (UvrA), and translesion synthesis (UmuC/D) are essential for maintaining mutagenesis and culturability, while others (RecN, RmuC) have limited impact. Notably, deletion of UvrD (a repair-associated helicase) intensifies transient non-culturability without affecting mutagenesis, underscoring complexity in repair networks. Overall, our findings reveal a dose-dependent trade-off: moderate UV-B promotes mutagenesis with minimal viability loss, whereas prolonged exposure suppresses mutagenesis via transient dormancy, reflecting an adaptive strategy with significant evolutionary implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fast evolution of SOS-independent multi-drug resistance in bacteria.Elife. 2025 Jul 9;13:RP95058. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95058. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40631979 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Optimisation of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for untreated Hodgkin lymphoma patients with respect to second malignant neoplasms, overall and progression-free survival: individual participant data analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 13;9(9):CD008814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008814.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28901021 Free PMC article.
-
Carboplatin and paclitaxel induced-gonadotoxicity on the ovarian reserve of young breast cancer patients with BRCA1 mutation.Hum Reprod. 2025 Jul 11:deaf133. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf133. Online ahead of print. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40646715
References
-
- MacLean R. C., Torres-Barceló C. & Moxon R. Evaluating evolutionary models of stress-induced mutagenesis in bacteria. Nature Reviews Genetics 2013 14:3 14, 221–227 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
