This is a preprint.
A reference genome for Trichogramma kaykai: A tiny desert-dwelling parasitoid wasp with competing sex-ratio distorters
- PMID: 39605481
- PMCID: PMC11601539
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.22.624848
A reference genome for Trichogramma kaykai: A tiny desert-dwelling parasitoid wasp with competing sex-ratio distorters
Update in
-
A reference genome for Trichogramma kaykai: a tiny desert-dwelling parasitoid wasp with competing sex-ratio distorters.G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Aug 6;15(8):jkaf129. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf129. G3 (Bethesda). 2025. PMID: 40476364 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The tiny parasitoid wasp Trichogramma kaykai inhabits the Mojave Desert of the southwest United States. Populations of this tiny insect variably host up to two different sex-distorting genetic elements: (1) the endosymbiotic bacterium Wolbachia which induces the parthenogenetic reproduction of females, and (2) a B-chromosome, "Paternal Sex Ratio" (PSR), which converts would-be female offspring to PSR-transmitting males. We report here the genome of a Wolbachia-infected Trichogramma kaykai isofemale colony KSX58. Using Oxford Nanopore sequencing we produced a final genome assembly of 203 Mbp with 45x coverage, consisting of 213 contigs with an N50 of 1.9 Mbp. The assembly is quite complete, with 91.41% complete BUSCOs recovered: a very high score for Trichogrammatids that have been previously characterized for having high levels of core gene losses. We also report a complete mitochondrial genome for T. kaykai, and an assembly of the associated Wolbachia, strain wTkk. We identified copies of the parthenogenesis-inducing genes pifA and pifB in a remnant prophage region of the wTkk genome. The Trichogramma kaykai assembly is the highest quality genome assembly for the genus to-date and will serve as a great resource for understanding the evolution of sex and selfish genetic elements.
Keywords: B chromosome; Trichogramma kaykai; Wolbachia; selfish genetic element; sex ratio; symbiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Statement The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

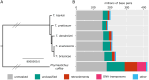


References
-
- Almeida R., and Stouthamer R., 2017. Phylogeny of the Trichogramma endosymbiont Wolbachia, an alpha-proteobacteria (Rickettsiae). Braz. J. Biol. 78 (03): 421–428. - PubMed
-
- Bailly-Bechet M., Martins-Simões P., Szöllősi G. J., Mialdea G., Sagot M.-F. et al. , 2017. How long does Wolbachia remain on board? Mol. Biol. Evol. 34 (5): 1183–1193. - PubMed
-
- Bernt M., Donath A., Jühling F., Externbrink F., Florentz C. et al. , 2013. MITOS: improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 69 (2): 313–319. - PubMed
-
- Beukeboom L. W., and Van De Zande L., 2010. Genetics of sex determination in the haplodiploid wasp Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea). Journal of Genetics 89: 333–339. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
