This is a preprint.
International multi-cohort analysis identifies novel framework for quantifying immune dysregulation in critical illness: results of the SUBSPACE consortium
- PMID: 39605502
- PMCID: PMC11601436
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.12.623298
International multi-cohort analysis identifies novel framework for quantifying immune dysregulation in critical illness: results of the SUBSPACE consortium
Update in
-
A consensus immune dysregulation framework for sepsis and critical illnesses.Nat Med. 2025 Dec;31(12):4084-4096. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03956-5. Epub 2025 Sep 30. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 41028543 Free PMC article.
Abstract
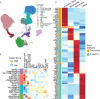
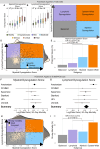
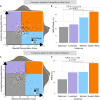
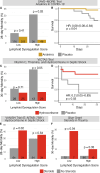
Progress in the management of critical care syndromes such as sepsis, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), and trauma has slowed over the last two decades, limited by the inherent heterogeneity within syndromic illnesses. Numerous immune endotypes have been proposed in sepsis and critical care, however the overlap of the endotypes is unclear, limiting clinical translation. The SUBSPACE consortium is an international consortium that aims to advance precision medicine through the sharing of transcriptomic data. By evaluating the overlap of existing immune endotypes in sepsis across over 6,000 samples, we developed cell-type specific signatures to quantify dysregulation in these immune compartments. Myeloid and lymphoid dysregulation were associated with disease severity and mortality across all cohorts. This dysregulation was not only observed in sepsis but also in ARDS, trauma, and burn patients, indicating a conserved mechanism across various critical illness syndromes. Moreover, analysis of randomized controlled trial data revealed that myeloid and lymphoid dysregulation is linked to differential mortality in patients treated with anakinra or corticosteroids, underscoring its prognostic and therapeutic significance. In conclusion, this novel immunology-based framework for quantifying cellular compartment dysregulation offers a valuable tool for prognosis and therapeutic decision-making in critical illness.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest NJM reports consulting fees from Novartis, Inc, AstraZeneca, Inc, and Endpoint Health, Inc (>2 years ago) YH is employed by Inflammatix, Inc. PK is co-founder, consultant to, and a scientific advisor to Inflammatix, Inc. TES is co-founder and CEO of Inflammatix, Inc. All other authors report no disclosures or conflicts of interest
Figures


References
-
- Berthelsen P. G. & Cronqvist M. The first intensive care unit in the world: Copenhagen 1953. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 47, 1190–1195 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Maslove D. M. et al. Redefining critical illness. Nat. Med. 28, 1141–1148 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Marshall J. C. Why have clinical trials in sepsis failed? Trends Mol. Med. 20, 195–203 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
