This is a preprint.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the EGFR Ligand Epiregulin Elicit Robust Anti-Tumor Activity in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 39605519
- PMCID: PMC11601497
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.20.581056
Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the EGFR Ligand Epiregulin Elicit Robust Anti-Tumor Activity in Colorectal Cancer
Update in
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the EGFR Ligand Epiregulin Elicit Robust Antitumor Activity in Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 3;85(5):973-986. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-0798. Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39693606 Free PMC article.
Abstract
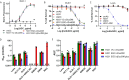
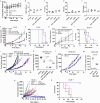
As colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related death, identifying therapeutic targets and approaches is essential to improve patient outcomes. The EGFR ligand epiregulin (EREG) is highly expressed in RAS wildtype and mutant CRC with minimal expression in normal tissues, making it an attractive target for antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) development. In this study, we produced and purified an EREG monoclonal antibody (mAb), H231, that had high specificity and affinity for human and mouse EREG. H231 also internalized to lysosomes, which is important for ADC payload release. ImmunoPET and ex vivo biodistribution studies showed significant tumor uptake of 89Zr-labeled H231 with minimal uptake in normal tissues. H231 was conjugated to either cleavable dipeptide or tripeptide chemical linkers attached to the DNA-alkylating payload duocarmycin DM, and cytotoxicity of EREG ADCs was assessed in a panel of CRC cell lines. EREG ADCs incorporating tripeptide linkers demonstrated the highest potency in EREG-expressing CRC cells irrespective of RAS mutations. Preclinical safety and efficacy studies showed EREG ADCs were well-tolerated, neutralized EGFR pathway activity, caused significant tumor growth inhibition or regression, and increased survival in CRC cell line and patient-derived xenograft models. These data suggest EREG is a promising target for the development of ADCs for treating CRC and other cancer types that express high levels of EREG. While the efficacy of clinically approved anti-EGFR mAbs are largely limited by RAS mutational status, EREG ADCs may show promise for both RAS mutant and wildtype patients, thus improving existing treatment options.
Keywords: Epiregulin; RAS; antibody-drug conjugate; colorectal cancer; patient-derived xenograft models.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Y.A. and K.T. are named inventors on all or some of the patent applications (WO2018218004A1, US11629122B2, EP3630189A4 and WO2023122587A3) relating to the linker technologies described in this article. K.T. is a co-founder of and holds equity in CrossBridge Bio. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023;73:233–54 - PubMed
-
- Fakih MG, Salvatore L, Esaki T, Modest DP, Lopez-Bravo DP, Taieb J, et al. Sotorasib plus Panitumumab in Refractory Colorectal Cancer with Mutated KRAS G12C. N Engl J Med 2023;389:2125–39 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
