This is a preprint.
ATR safeguards replication forks against APOBEC3B-induced toxic PARP1 trapping
- PMID: 39605722
- PMCID: PMC11601322
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.14.623607
ATR safeguards replication forks against APOBEC3B-induced toxic PARP1 trapping
Update in
-
Mechanism of DNA replication fork breakage and PARP1 hyperactivation during replication catastrophe.Sci Adv. 2025 Apr 18;11(16):eadu0437. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu0437. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40238882
Abstract
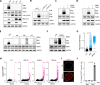
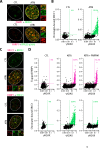
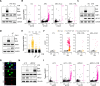
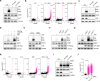
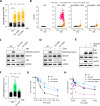
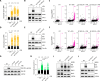
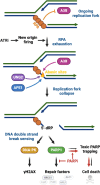
ATR is the master safeguard of genomic integrity during DNA replication. Acute inhibition of ATR with ATR inhibitor (ATRi) triggers a surge in origin firing, leading to increased levels of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) that rapidly deplete all available RPA. This leaves ssDNA unprotected and susceptible to breakage, a phenomenon known as replication catastrophe. However, the mechanism by which unprotected ssDNA breaks remains unclear. Here, we reveal that APOBEC3B is the key enzyme targeting unprotected ssDNA at replication forks, triggering a reaction cascade that induces fork collapse and PARP1 hyperactivation. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that uracils generated by APOBEC3B at replication forks are removed by UNG2, creating abasic sites that are subsequently cleaved by APE1 endonuclease. Moreover, we demonstrate that APE1-mediated DNA cleavage is the critical enzymatic step for PARP1 trapping and hyperactivation in cells, regardless of how abasic sites are generated on DNA. Finally, we show that APOBEC3B-induced toxic PARP1 trapping in response to ATRi drives cell sensitivity to ATR inhibition, creating to a context of synthetic lethality when combined with PARP inhibitors. Together, these findings reveal the mechanisms that cause replication forks to break during replication catastrophe and explain why ATRi-treated cells are particularly sensitive to PARP inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
