Transcriptomics profiling of the non-small cell lung cancer microenvironment across disease stages reveals dual immune cell-type behaviors
- PMID: 39606240
- PMCID: PMC11600981
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394965
Transcriptomics profiling of the non-small cell lung cancer microenvironment across disease stages reveals dual immune cell-type behaviors
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, with poor survival despite recent therapeutic advances. A better understanding of the complexity of the tumor microenvironment is needed to improve patients' outcome.
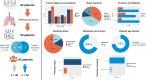
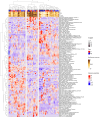
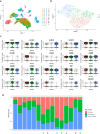
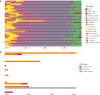
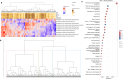
Methods: We applied a computational immunology approach (involving immune cell proportion estimation by deconvolution, transcription factor activity inference, pathways and immune scores estimations) in order to characterize bulk transcriptomics of 62 primary lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) samples from patients across disease stages. Focusing specifically on early stage samples, we validated our findings using an independent LUAD cohort with 70 bulk RNAseq and 15 scRNAseq datasets and on TCGA datasets.
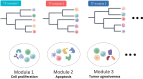
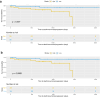
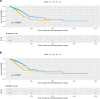
Results: Through our methodology and feature integration pipeline, we identified groups of immune cells related to disease stage as well as potential immune response or evasion and survival. More specifically, we reported a duality in the behavior of immune cells, notably natural killer (NK) cells, which was shown to be associated with survival and could be relevant for immune response or evasion. These distinct NK cell populations were further characterized using scRNAseq data, showing potential differences in their cytotoxic activity.
Conclusion: The dual profile of several immune cells, most notably T-cell populations, have been discussed in the context of diseases such as cancer. Here, we report the duality of NK cells which should be taken into account in conjunction with other immune cell populations and behaviors in predicting prognosis, immune response or evasion.
Keywords: cell deconvolution; immune landscape; lung adenocarcinoma; natural killer cells; transcription factor activity.
Copyright © 2024 Hurtado, Khajavi, Essabbar, Kammer, Xie, Coullomb, Pradines, Casanova, Kruczynski, Gouin, Clermont, Boutillet, Senosain, Zou, Zhao, Burq, Mahfoudi, Besse, Launay, Passioukov, Chetaille, Favre, Maldonado, Cruzalegui, Delfour, Mazières and Pancaldi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures





References
-
- Merotto L, Zopoglou M, Zackl C, Finotello F. Next-generation deconvolution of transcriptomic data to investigate the tumor microenvironment. In: International review of cell and molecular biology. Academic Press; (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

