This is a preprint.
Identification of a Resistance Exercise-Specific Signaling Pathway that Drives Skeletal Muscle Growth
- PMID: 39606434
- PMCID: PMC11601848
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4997138/v1
Identification of a Resistance Exercise-Specific Signaling Pathway that Drives Skeletal Muscle Growth
Update in
-
Identification of a resistance-exercise-specific signalling pathway that drives skeletal muscle growth.Nat Metab. 2025 Jul;7(7):1404-1423. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01298-7. Epub 2025 May 15. Nat Metab. 2025. PMID: 40374925 Free PMC article.
Abstract
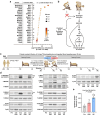
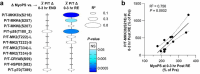
A human model of unilateral endurance versus resistance exercise, in conjunction with deep phosphoproteomic analyses, was used to identify exercise mode-specific phosphorylation events. Among the outcomes, a resistance exercise-specific cluster of events was identified, and a multitude of bioinformatic- and literature-based predictions suggested that this was mediated by prolonged activation of a pathway involving MKK3b/6, p38, MK2, and mTORC1. Follow-up studies in humans and mice provide consistent support for the predictions and also revealed that resistance exercise-induced signaling through MKK3b and the induction of protein synthesis are highly correlated events (R = 0.87). Moreover, genetic activation of MKK3b/6 in skeletal muscles was sufficient to induce signaling through the members of the resistance exercise-specific pathway, as well as an increase in protein synthesis and fiber size. Thus, we propose that we have identified some of the core components of a signaling pathway that drives the growth-promoting effects of resistance exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Declarations: Yes there is potential Competing Interest. Troy A. Hornberger received a research grant from Novo Nordisk. This could be perceived as a potential conflict of interest, however, Novo Nordisk and Troy A. Hornberger do not have any agreements that could lead to a financial gain or loss from this publication.
Figures






References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

