This is a preprint.
Isoaspartate formation and irreversible aggregation of collapsin response mediator protein 2: implications for the etiology of epilepsy and age-related cognitive decline
- PMID: 39606475
- PMCID: PMC11601837
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5074866/v1
Isoaspartate formation and irreversible aggregation of collapsin response mediator protein 2: implications for the etiology of epilepsy and age-related cognitive decline
Update in
-
Isoaspartate formation and irreversible aggregation of collapsin response mediator protein 2: implications for the etiology of epilepsy and age-related cognitive decline.Amino Acids. 2024 Dec 24;57(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03435-0. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 39719537 Free PMC article.
Abstract
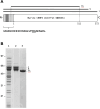
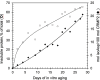
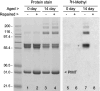
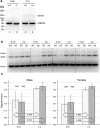
Collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) functions in the genesis and activity of neuronal connections in mammalian brain. We previously reported that a protein coincident with CRMP2 on 2D-gels undergoes marked accumulation of abnormal L-isoaspartyl sites in brain extracts of mice missing the repair enzyme, protein L-isoaspartyl methyltransferase (PIMT). To conflrm and explore the signiflcance of isoaspartyl damage in CRMP2, we expressed and purifled recombinant mouse CRMP2 (rCRMP2). A polyclonal antibody made against the recombinant protein precipitated CRMP2 from brain extracts of PIMT-KO mice, but not from WT mice, suggesting that (1) the rCRMP2 antigen underwent signiflcant isoAsp formation in the process of antibody production and (2) the isoAsp form of CRMP2 is considerably more immunogenic than the native protein. In vitro aging of rCRMP2 at pH 7.4, 37°C for 0-28 days led to robust accumulation of isoAsp sites that were repairable by PIMT, and also induced a progressive accumulation of apparent dimers and higher-mass oligomers as judged by SDS-PAGE. A similar pattern of CRMP2 aggregation was observed in mice, with levels increasing throughout the lifespan. We conclude that CRMP2 is indeed a major target of PIMT-mediated protein repair in the brain; that isoAsp forms of CRMP2 are highly immunogeni; and that CRMP2 dysfunction makes a signiflcant contribution to neuropathology in the PIMT-KO mouse.
Keywords: aging; autoimmunity – epilepsy; protein aggregation; protein damage; protein repair.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests. Additional Declarations: No competing interests reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Isoaspartate formation and irreversible aggregation of collapsin response mediator protein 2: implications for the etiology of epilepsy and age-related cognitive decline.Amino Acids. 2024 Dec 24;57(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03435-0. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 39719537 Free PMC article.
-
Isoaspartate accumulation in mouse brain is associated with altered patterns of protein phosphorylation and acetylation, some of which are highly sex-dependent.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 5;8(11):e80758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080758. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24224061 Free PMC article.
-
Isoaspartyl formation in creatine kinase B is associated with loss of enzymatic activity; implications for the linkage of isoaspartate accumulation and neurological dysfunction in the PIMT knockout mouse.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 23;9(6):e100622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100622. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24955845 Free PMC article.
-
PROTEIN l-ISOASPARTYL METHYLTRANSFERASE (PIMT) in plants: regulations and functions.Biochem J. 2020 Nov 27;477(22):4453-4471. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200794. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 33245750 Review.
-
PIMT-Mediated Protein Repair: Mechanism and Implications.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019 May;84(5):453-463. doi: 10.1134/S0006297919050018. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019. PMID: 31234761 Review.
References
-
- Arimura N., Inagaki N., Chihara K., Ménager C., Nakamura N., Amano M., Iwamatsu A., Goshima Y., & Kaibuchi K. (2000). Phosphorylation of collapsin response mediator protein-2 by Rho-kinase. Evidence for two separate signaling pathways for growth cone collapse. The Journal of biological chemistry, 275(31), 23973–23980. 10.1074/jbc.M001032200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arimura N., Ménager C., Kawano Y., Yoshimura T., Kawabata S., Hattori A., Fukata Y., Amano M., Goshima Y., Inagaki M., Morone N., Usukura J., & Kaibuchi K. (2005). Phosphorylation by Rho kinase regulates CRMP-2 activity in growth cones. Molecular and cellular biology, 25(22), 9973–9984. 10.1128/MCB.25.22.9973-9984.2005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bretin S., Reibel S., Charrier E., Maus-Moatti M., Auvergnon N., Thevenoux A., Glowinski J., Rogemond V., Prémont J., Honnorat J., & Gauchy C. (2005). Differential expression of CRMP1, CRMP2A, CRMP2B, and CRMP5 in axons or dendrites of distinct neurons in the mouse brain. The Journal of comparative neurology, 486(1), 1–17. 10.1002/cne.20465 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

